You may be using a RAID storage system for speed, data redundancy, or a combination of both. However, RAID drives are still susceptible to data loss. Due to the relatively complex nature of these storage systems, RAID data recovery is trickier than standard hard disk drives. It’s important to choose a good RAID data recovery program if you want to safely recover data from a RAID array.
Specifics of RAID Data Recovery
RAID data recovery significantly differs from regular data recovery from a hard drive or SSD. In most cases of data loss in a RAID, you will need to rebuild the RAID drive to its original parameters. This can be done by using specialized software or using professional help.
Note: If your RAID is completely inaccessible, it’s recommended you contact a professional data recovery service. A failed RAID rebuild attempt will cause further data loss.
A crucial step in RAID array recovery is knowing which RAID level are you using. The most common RAID configurations include:
RAID Type | Description |
RAID 0 | RAID 0 works on the principle of “striping” data across multiple disks, i.e. data is split across the drives, resulting in exponentially fast read and write speeds. While this is good for performance, RAID 0 doesn’t offer any data redundancy because even if one of the drives fail, all your data is rendered corrupt and inaccessible. |
RAID 1 | A RAID 1 array mirrors the data on your drives. Essentially, your data is copied exactly as it is to all the drives in the RAID array, making RAID 1 excellent for data redundancy. A major drawback is that users only get half the effective storage space at double the cost. |
RAID 5 | A level 5 RAID array stripes your data across the drives. In addition to that, it stores a parity checksum, a sort of integrity check for the data, on a separate drive. This allows the data to be striped across the hard drives, while providing data redundancy in case one of them fails. You need at least three hard drives to set up a RAID 5 array. |
RAID 6 | A RAID 6 array works on the same principle as RAID 5. However, it uses two parity blocks to keep a check on the data. This means that a RAID 6 array can survive two hard disk failures without losing data. RAID 6 requires at least four storage drives in order to work. |
RAID storage systems either use a software or a hardware controller to ensure the RAID arrays work together. A common reason behind RAID data loss is a corrupt or failing RAID controller. One telltale sign of this is data loss, even though all individual drives are in full working order.
Some RAID enclosures come with an eSATA or USB interface that lets them connect directly to a PC. But, if the RAID array is damaged, not detected by the PC, or there’s no compatible connection interface on the enclosure, you will have to manually rebuild the RAID array. The RAID rebuild process will take place on the PC you’ll use to perform RAID data recovery.
What Is Nested RAID
Explained above, are the basic RAID levels. But, you can combine two different RAID types according to your specific use case. This is called a nested or hybrid RAID. While there are various hybrid RAID types, the most common one is RAID 10 (RAID 1 + RAID 0).
RAID 10 combines the mirroring of RAID 0, with the data striping of RAID 1. A RAID 10 setup requires four disks and can survive two failed disks. Due to their nature, nested RAIDs require more number of disks than their regular counterparts.
Other nested RAID types include RAID 50 (RAID 5 + RAID 0) and RAID 60 (RAID 6 and RAID 0), which require a minimum of six and eight storage drives respectively.
Top 7 Best RAID Data Recovery Tools
RAID file recovery is complex, which makes it imperative that you choose a RAID recovery tool that caters to your particular RAID type and data loss scenario. To make your job easier, we’ve compiled a list of the best RAID data recovery programs along with necessary information such as the supported RAID levels, file systems, and operating systems.
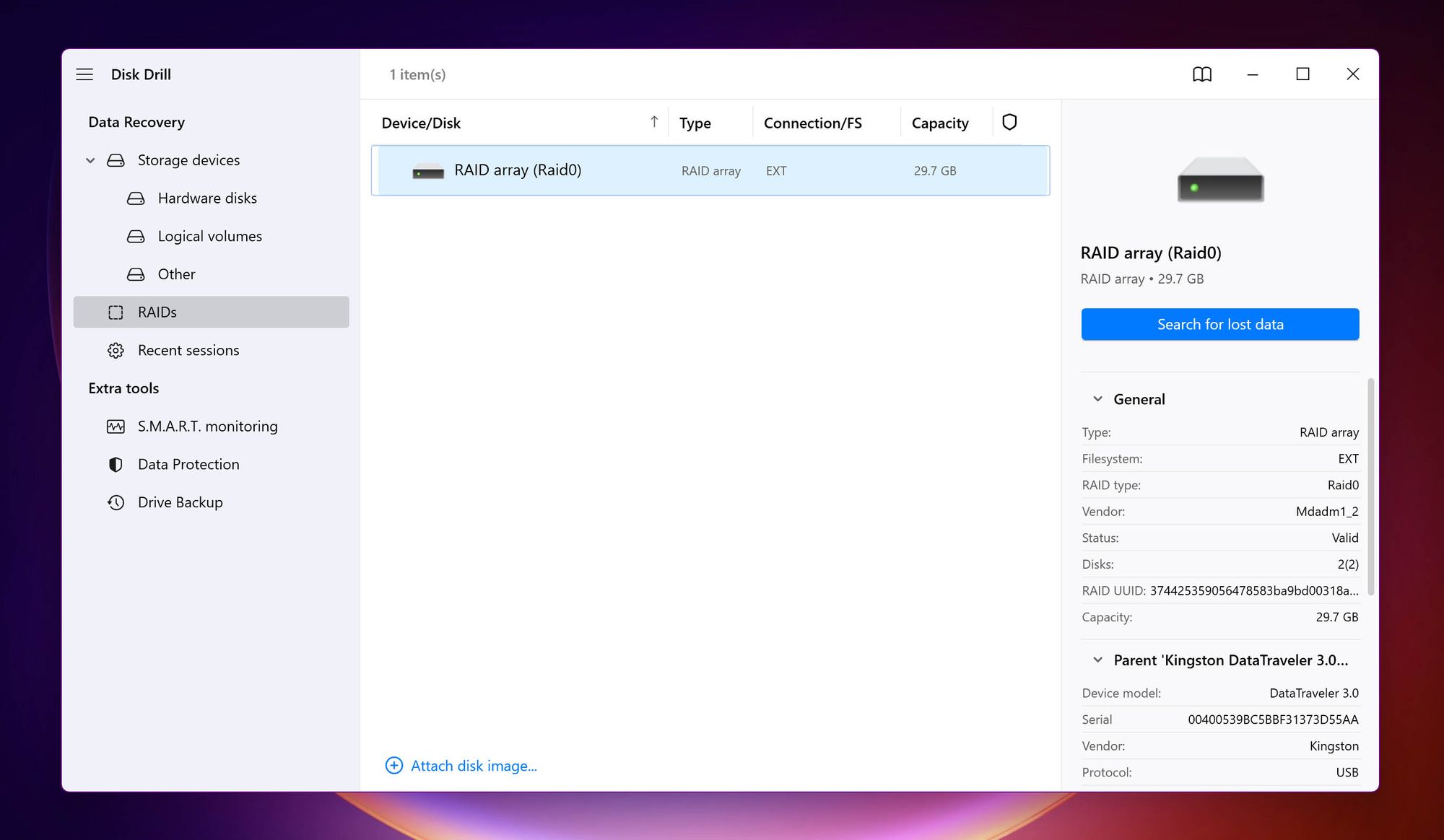
1. Disk Drill
- 🗂️ Supported File Systems: FAT16 / FAT32, exFAT, NTFS / NTFS5, HFS / HFS+, APFS, ReFS, ext2 / ext3 / ext4
- ⚙️ Operating System Compatibility: Windows and macOS.
- 📊 Supported RAID Levels: Disk Drill for Windows and macOS supports Windows and Linux RAID levels such as RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 10, RAID 1E RAID 5, RAID 6, JBOD. Only Disk Drill for macOS supports Apple RAID levels such as RAID 0, RAID 1, JBOD.
- 💰 Price: Disk Drill costs $89 for a lifetime license.
Disk Drill appears in several lists of the best data recovery apps in the market, and for good reason. In addition to Disk Drill’s excellent data recovery rate, the emphasis on user-friendliness makes data recovery from RAID drives a breeze. To recover data from a RAID setup, you simply need to:
- Connect the RAID setup to your PC.
- Open Disk Drill, and choose the RAIDs option on the left navigation bar.
- Select the RAID and click Search for lost data.
Most data recovery software vendors, including Disk Drill recommend that you connect the drives directly to your computer. Likewise, some NAS/RAID enclosures have USB/eSATA connectors that let you connect the array to your PC, eliminating the need to connect individual drives.
For an in-depth look at the program, be sure to check out our Disk Drill data recovery review.
Pros
- The modular, easy to use interface makes Disk Drill suitable for beginners and experts alike.
- It lets you create a RAID disk image using the Byte-to-byte backup feature. You need to create individual disk images of each drive in the array, then attach the disk images to Disk Drill, and simply scan them as a RAID array.
- Excellent data recovery rate.
- Fast scan speeds.
- Filter recoverable files by type, size, recovery chances, and more.
Cons
- It does not support file systems such as XFS, ZFS, BTRFS, which are commonly found in NAS devices.
- Disk Drill cannot rebuild a RAID.
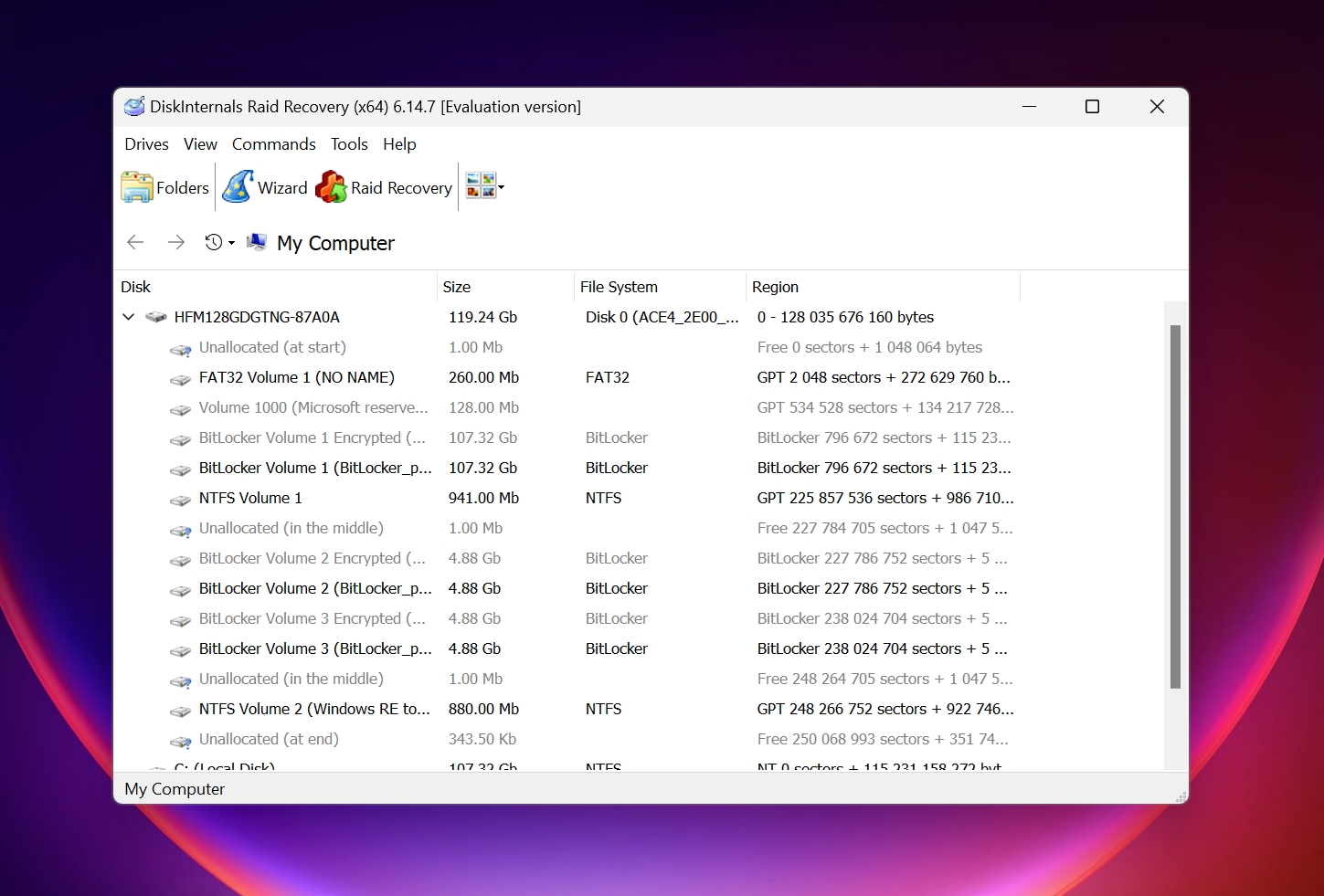
2. DiskInternals
- 🗂️ Supported File Systems: FAT16 / FAT32, exFAT, NTFS / NTFS5, HFS / HFS+, APFS, ReFS, ext2 / ext3 / ext4
- ⚙️ Operating System Compatibility: Windows
- 📊 Supported RAID Levels: RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 0+1, RAID 1E, RAID 5, RAID 50, RAID 5EE, RAID 5R, RAID 4, RAID6, RAID 60, JBOD, Microsoft RAID, MS Storage Spaces, Apple RAID, Linux RAID, ZFS RAIDZ, ZFS RAIDZ2
- 💰 Price: DiskInternals costs $249, $499, and $899 for data recovery from RAID arrays with up to 3, 6, and 8 disks respectively. For more than 8 disks, you will need to purchase the $1299 license.
DiskInternals RAID Recovery is quite adept at automatically detecting and rebuilding RAID arrays. The wizard-based data recovery process ensures that you don’t feel lost at any point while using the program. However, users should be prepared to wait, as RAID rebuilding and scanning takes a long time.
The primary area where DiskInternals falls short, is its pricing structure. While the pricing plans start at $249, they’re designed in a way that you’ll likely have to pay more to take full advantage of the program.
Pros
- Automatically detects and rebuilds RAID arrays.
- Supports a wide range of RAID types.
- There are two scan types available to the user–Fast Recovery Mode and Full Recovery Mode.
Cons
- Very pricey.
- Slow scan speeds.
- The free trial includes file preview, but not file recovery.
- Only compatible with Windows.
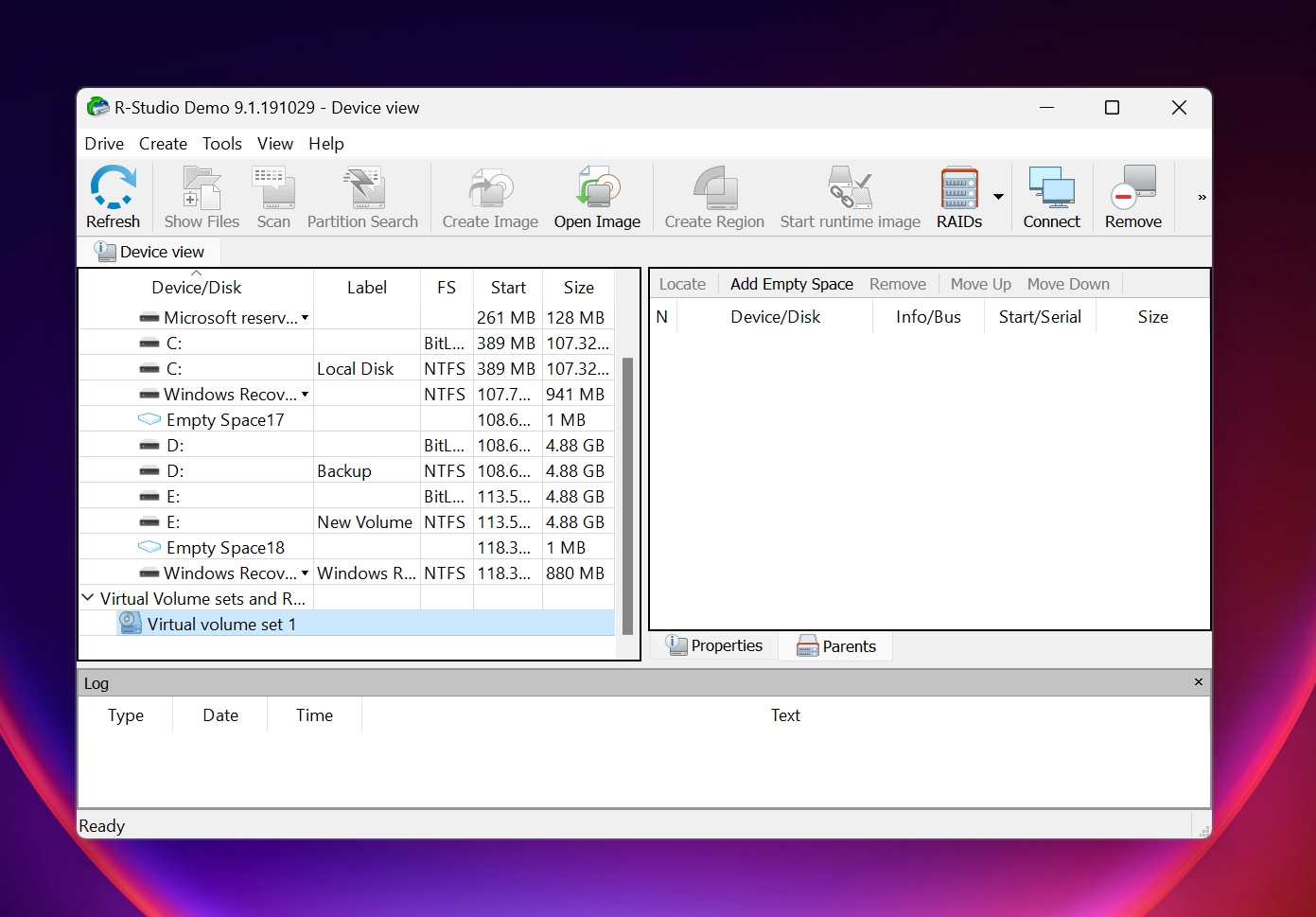
3. R-Studio
- 🗂️ Supported File Systems: NTFS, NTFS5, ReFS, FAT12/16/32, exFAT, HFS/HFS+, APFS, XFS, UFS1/UFS2 (FreeBSD/OpenBSD/NetBSD/Solaris) and Ext2/Ext3/Ext4 FS (Linux)
- ⚙️ Operating System Compatibility: Windows, macOS, and Ubuntu/Linux
- 📊 Supported RAID Levels: RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 4, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 10 (1+0), RAID1E, RAID5E, RAID5EE, RAID6E, Custom Windows, Mac, and Linux RAID configurations.
- 💰 Price: Starts at $54.99, up to $899, depending on your needs.
A major name in the data recovery software world, R-Studio is an excellent choice for seasoned PC users and has numerous good recovery reviews across the web. It supports almost all RAID configurations under the sun, with support for custom RAIDs. A standout feature of R Studio, is its ability to create and recover data from virtual RAIDs. This lets you create a virtual copy and structure of the original RAID, in case the data loss was caused by severe corruption or drive failure and resulted in a faulty RAID.
The R-Studio user interface is complex, which may deter beginner PC users from using it. There is no stone left unturned when it comes to the sheer number of features on offer, but only technically proficient users will be able to use R-Studio to its full potential.
Pros
- Loaded with features.
- Create virtual RAID arrays, even if the original RAID configuration is faulty.
- Even though the program is difficult to use, R-Studio makes up for it with a detailed knowledge base.
- Supports custom file formats, even if R-Studio doesn’t recognize them natively.
Cons
- Complicated user interface.
- Doesn’t recover original file names and folder structures in many instances.
- You cannot view recoverable files until the scan is 100% complete.
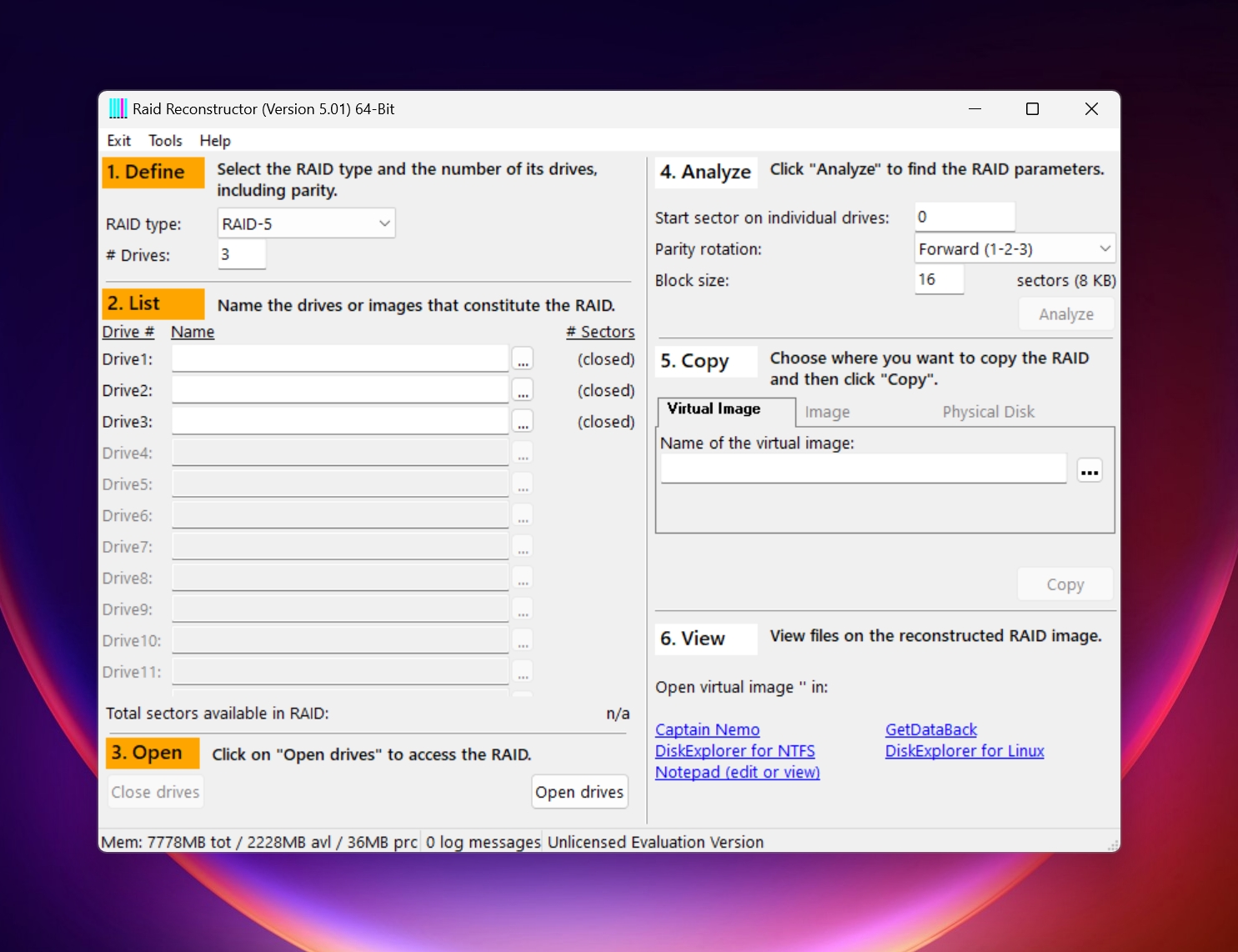
4. GetDataBack (RAID Reconstructor)
- 🗂️ Supported File Systems: NTFS, exFAT, FAT 12/16/32, EXT, HFS+, APFS.
- ⚙️ Operating System Compatibility: Windows
- 📊 Supported RAID Levels: RAID 0, RAID 5
- 💰 Price: $99 with free lifetime updates
Runtime Software’s RAID Reconstructor is a good companion to its data recovery counterpart, GetDataBack. You don’t need to know any RAID parameters to reconstruct your RAID setup using RAID Reconstructor. The software automatically analyzes your RAID drives and fills in the correct parameters. You can then create a virtual image of the RAID and use GetDataBack or some other data recovery program to recover the data.
At this time, RAID Reconstructor only supports RAID 0 and RAID 5 arrays.
Pros
- Automatically detects and fills in the RAID parameters.
- Supports up to 16 RAID drives.
- Read only design so you don’t lose any more data.
Cons
- Only supports RAID reconstruction, not RAID data recovery.
- Can only be used for RAID 0 and RAID 5 arrays.
- Doesn’t support NAS RAID arrays.
5. UFS Explorer
- 🗂️ Supported File Systems: NTFS, FAT, FAT32, exFAT, HFS+, APFS, Ext2, Ext3, Ext4, XFS, Extended format XFS, JFS, ReiserFS, UFS, UFS2, Adaptec UFS, big-endian UFS, Sun ZFS, BTRFS, BSD/Solaris: Simple/Stripe ZFS volumes
- ⚙️ Operating System Compatibility: Windows, macOS, and Linux
- 📊 Supported RAID Levels: RAID 0, RAID 1E, RAID 3, RAID 5, RAID 6, RAID 7, RAID 10, RAID 50, RAID 60 and other nested RAID levels, RAID 50E, ZFS, RAID-Z, RAID-Z2, RAID-Z3, Drobo BeyondRAID, Synology Hybrid RAID, BTRFS-RAID, MDADM, LVM, Apple Software RAID, Intel Matrix.
- 💰 Price: Starts at $139.95, up to $419.95, depending on the usage scenario.
UFS Explorer’s primary strength is its ability to recognize and recover data from almost every RAID combination imaginable. It automatically detects RAID parameters and virtually builds the RAID array. In case UFS Explorer RAID Recovery is unable to do that, you can use the RAID Builder tool within the UI to manually reconstruct the RAID array.
The program is only let down by its cluttered and unintuitive UI. It’s recommended that you refer to the UFS Explorer knowledge base before using the program.
Pros
- Recognizes all popular NAS vendors such as Drobo, Buffalo Technology (TeraStation, LinkStation), Synology, QNAP Systems, and more.
- Supports disk images.
- Can decrypt BitLocker and Apple APFS encrypted devices.
Cons
- Cluttered user interface.
- Expensive when compared to its competitors.
6. Hetman RAID Recovery
- 🗂️ Supported File Systems: FAT, exFAT, NTFS, ReFS, APFS, HFS+, Ext, ReiserFS, XFS, UFS, ZFS
- ⚙️ Operating System Compatibility: Windows
- 📊 Supported RAID Levels: JBOD, RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 10, RAID 1E, RAID 5, RAID 50, RAID 6, RAID 60, RAID 2, RAID 3, RAID 4
- 💰 Price: $97.95
Hetman RAID Recovery is targeted at non-technical users and makes rebuilding a RAID, simple. The UI is easy to use, and even though it offers a plethora of features, you will not feel overwhelmed with options. The program supports NAS devices and can auto-rebuild the RAID, in case your NAS controller fails. In case a RAID drive fails within the array, you can connect it separately and recover the data as well.
The scan speeds of Hetman RAID Recovery are not the best, and scanning large RAID arrays may take a long time.
Pros
- Easy to use, while being feature loaded.
- Contains many stored presets of array combinations used by popular controller manufacturers. This saves time.
- Supports all major RAID levels.
- There is a portable version of the program too.
Cons
- Can only be installed on a Windows machine.
- The free trial doesn’t let you recover any files, only view them.
7. Klennet Recovery
- 🗂️ Supported File Systems: FAT16/32, exFAT, NTFS, ext 2/3/4 XFS 4/5
- ⚙️ Operating System Compatibility: Windows 10 and above.
- 📊 Supported RAID Levels: RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5.
- 💰 Price: Starts at $49.
With an installer size of only 1800 KB, Klennet Recovery is a bite-sized Windows 10 RAID recovery program. It supports data recovery from RAID 0, RAID 1, and RAID 5 level arrays. The program can also determine disk orders for RAID 0 and RAID 5.
Klennet Recovery is a successor to Zero Assumption recovery, which was around for more than 20 years before being discontinued. But, Klennet Recovery still lacks support for various common RAID levels and file systems, making it useful in very limited RAID data loss scenarios.
Pros
- Easy to use.
- Can create disk images.
- It has a file preview feature.
- Small installation size.
Cons
- Only works on Windows 10 and above.
- Limited file system and RAID level support.
FAQ
How to recover data from RAID drives?
Here is a quick guide on how to recover files from a RAID array:
- Download and install Disk Drill.
- Connect the RAID set if possible, else connect the individual drives to your computer.
- Open Disk Drill, select the drive and click Search for lost data.
- Click Review found items.
- Select the desired files and click Recover.
How much does RAID recovery cost?
It’s difficult to find good free RAID recovery software, so be prepared to shell out anywhere from $50 to $899, depending on the program. Professional RAID data recovery services are substantially more expensive, ranging from $300 to more than $2000, depending on the severity of the data loss and the complexity of the array.
Is RAID better than backup?
No, it’s recommended you use good data backup tools to back up your data separately to other storage drives as well as the cloud. RAIDs can serve as an added protective measure.
Which RAID method is best?
Different RAID levels serve different purposes. Selecting the best RAID level will depend on your specific needs, and the usage scenario. You can take advantage of nested RAIDs to get the best of both worlds, but be prepared to spend more money.
Conclusion
It’s important to choose a good RAID data recovery program due to the cost and importance of data involved in RAID arrays. Additionally, remember to act as quickly as you can because multiple drives failing one after the other is not as rare as you may think.
This article was written by Manuviraj Godara, a Staff Writer at Handy Recovery Advisor. It was also verified for technical accuracy by Andrey Vasilyev, our editorial advisor.
Curious about our content creation process? Take a look at our Editor Guidelines.
