Tried to download a file to your computer, only to be met with a message stating that there’s no more space left on your hard drive? This may come as a surprise, especially when you check for large files to remove and find none.
This problem can occur on both HDDs and SSDs, and can pose a real problem if left unaddressed as it likely points to a more complicated issue. We’ll show you how to get everything sorted if your hard disk is full but no files are present.
Why Is My Disk Space Full But There Are No Files on It?
There are a number of reasons why this message can appear, both on your system drive and any other drive connected to your PC. We’ve briefly explained some of the most common ones below.
Reasons |
Description |
Hard drive errors |
Hard drive errors can manifest in a number of ways, like file system corruption or bad sectors. When a hard drive contains errors, it should be considered unstable and you should perform a full backup as soon as possible. |
File system corruption |
A corrupted file system is unusable, and any attempt to write new data to the partition will be rejected if that’s the case. We recommend performing data recovery as soon as possible. See our guide on how to recover data from a corrupted partition for more information. |
Reserved Storage |
Windows automatically reserves around 7 GB of space on your hard drive for temporary files and Windows updates. On smaller drives, it will only take 2% of the system volume or 3 GB of disk space, whichever is lower. Some of this space is also occupied by optional features. |
System Restore points |
Restore points are saved to help you restore your system to working order if something goes wrong. The amount of space reserved for restore points may be too large, resulting in them taking up too much space. This is commonly experienced on the system drive, where restore points are stored. |
Malware or viruses |
Although antimalware software is always evolving, viruses will always find ways to circumvent it. Viruses can be written to take up unnecessary space on your drive, preventing you from storing any more files. |
Hidden or system files |
Hidden data still takes up space on your drive, even if you can’t see it. The same goes for unnecessary system files that have been left over from previous updates or system processes, as they may not be deleted automatically once they’re no longer needed on your system drive. |
If a separate storage device is experiencing these problems, you won’t be able to write any more data to them. The same goes with your system drive, though you may notice additional problems during your regular use of Windows due to the lack of storage space. Either way, it’s best that you secure what data you can to protect it if the drive becomes more unstable.
Secure Important Data Data on a Hard Drive That’s Almost Full but Files Can’t Be Found
Knowing what caused this error to appear on your local disk is a good start, but before you jump into troubleshooting, it’s best that you retrieve all necessary data from the drive before you implement any fixes, especially if the drive is unstable. If the condition of your hard drive were to worsen while fixing it, some of your data may become irreversibly lost.
For this, we recommend Disk Drill. Disk Drill is a data recovery tool that is useful for recovering lost or existing data from basically any file system, including FAT16/32/exFAT, NTFS, HFS, HFS+, APFS, and EXT2/3/4. It also supports recovery from corrupted and RAW drives. You can learn more about the program in our extensive Disk Drill review.
Here’s how to recover data from a hard drive that’s almost full using Disk Drill:
- Download and install Disk Drill.
- Select the drive that’s experiencing the ‘hard disk full but no files’ problem. Click Search for lost data.
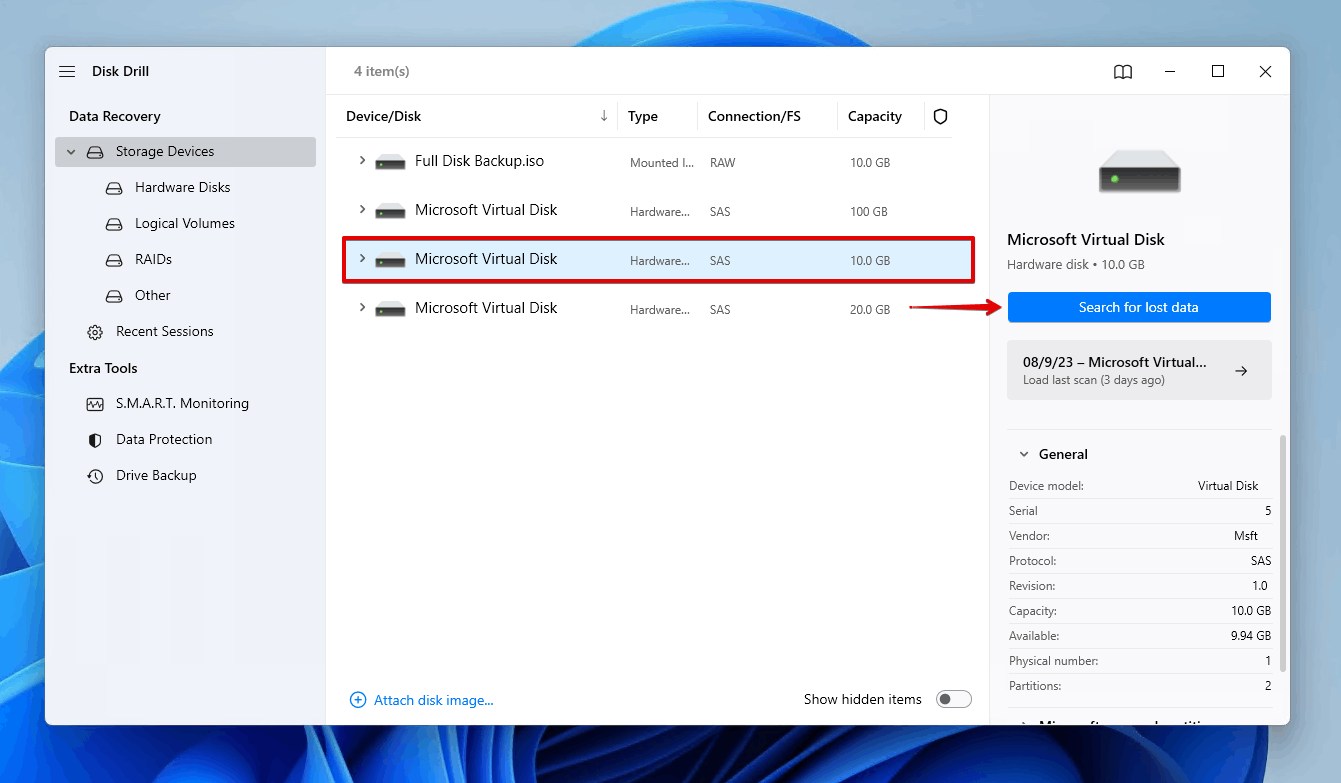
- Click Review found items. Optionally, you can click Recover all to restore everything that Disk Drill finds with its scan.
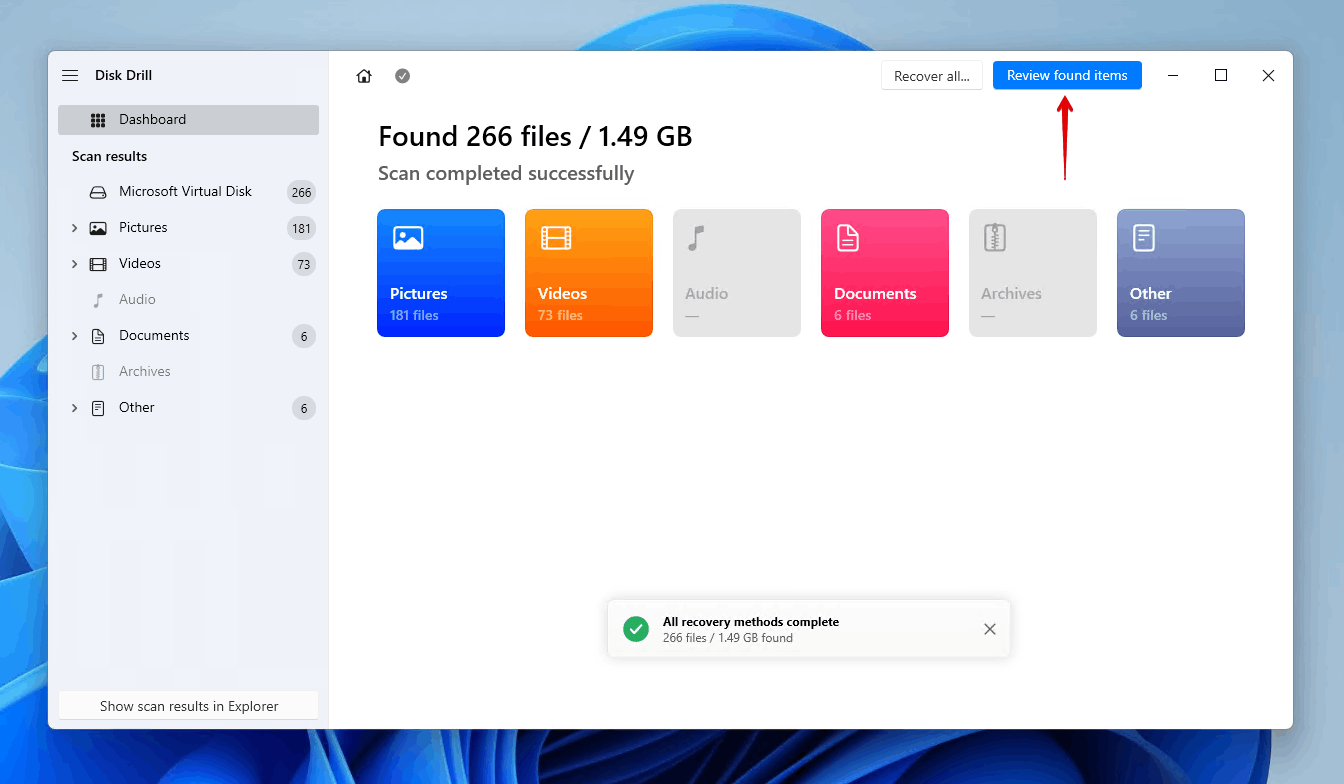
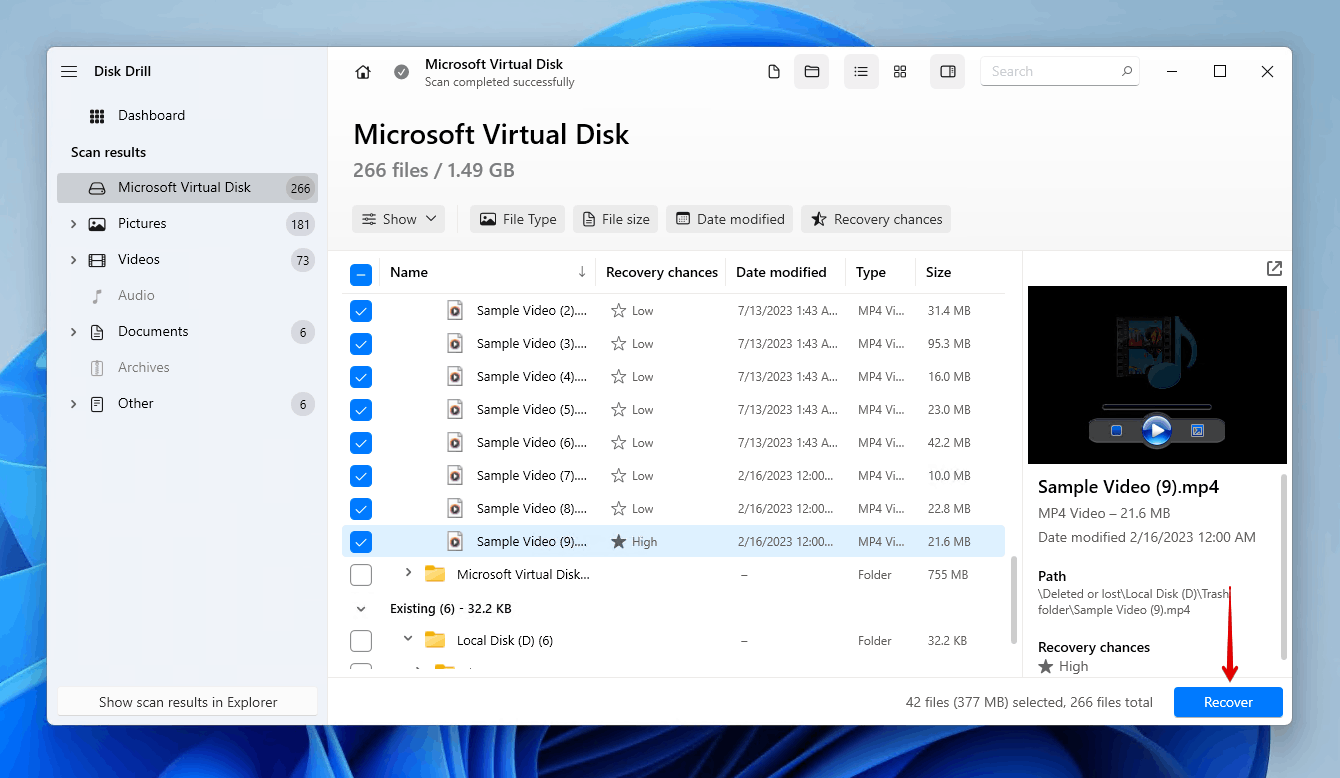
- Select the files you want to restore. Your data may be split between the Deleted or lost, Existing, or Reconstructed sections, depending on each file’s state. Also pay attention to the recovery chances column, as it will tell you which data is in a condition to be recovered. When ready, click Recover.
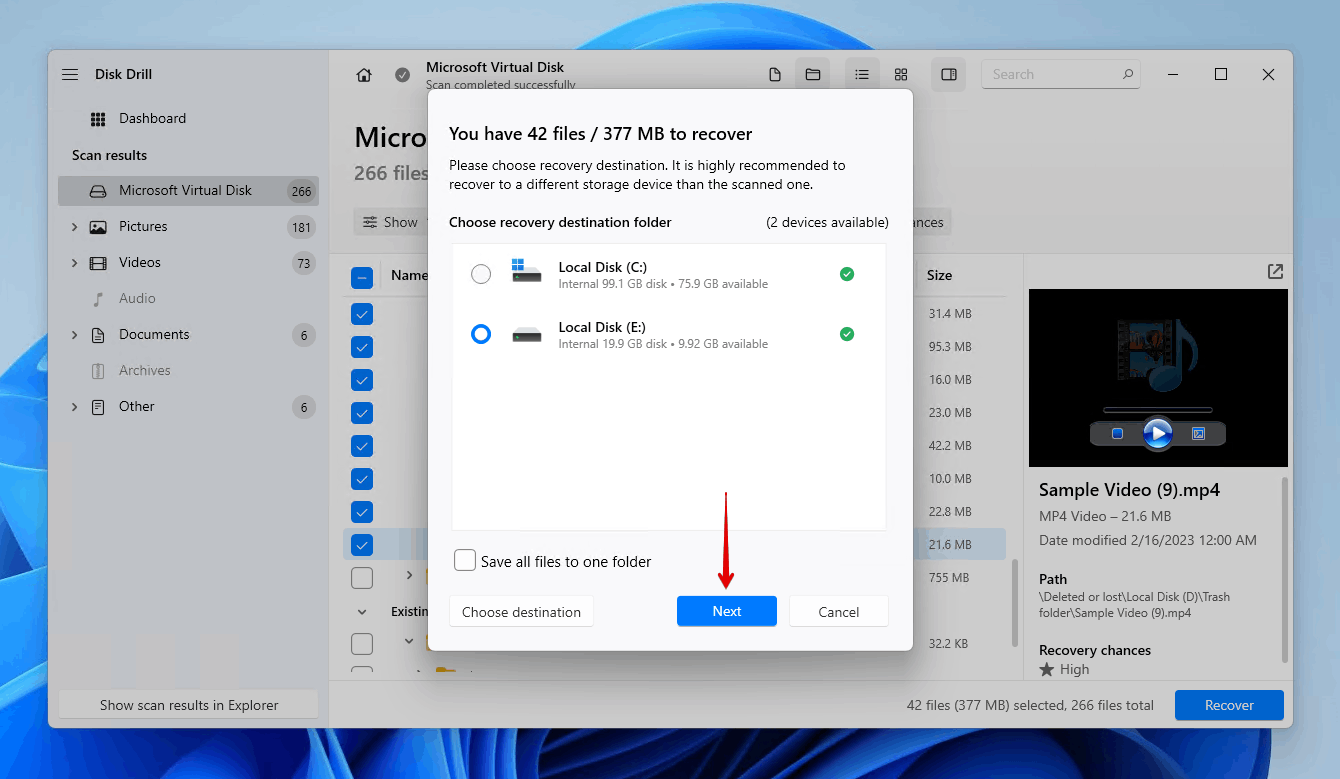
- Choose a safe recovery location on a separate storage device, then click Next.
Disk Drill is a great recovery tool, but it only allows you to recover up to 500 MB of your data without a Disk Drill PRO license. If you can’t invest in a paid solution right now, there are free ones that you can find on our list of the best data recovery software.
How to Fix ‘Hard Disk Full But No Files’ Error
With your data secure, let’s look at some of the ways you can fix the ‘hard drive full but no files’ error.
Method 1: Empty Recycle Bin
When you delete a file, it’s sent to Recycle Bin before being permanently deleted. This gives you the opportunity to restore something you’ve deleted before it’s too late. As deleted files build up, your Recycle Bin may end up taking up more space on your drive than you’d like.
External hard drive’s have their own Recycle Bin you can recover data from. See our guide on how to access the Recycle Bin on an external hard drive for more details.
Here’s how you can address low disk space by emptying Recycle Bin. Bear in mind that it’s always a good idea to check Recycle Bin first to see if you want to keep any of the data inside it, as the following instructions will delete anything it contains.
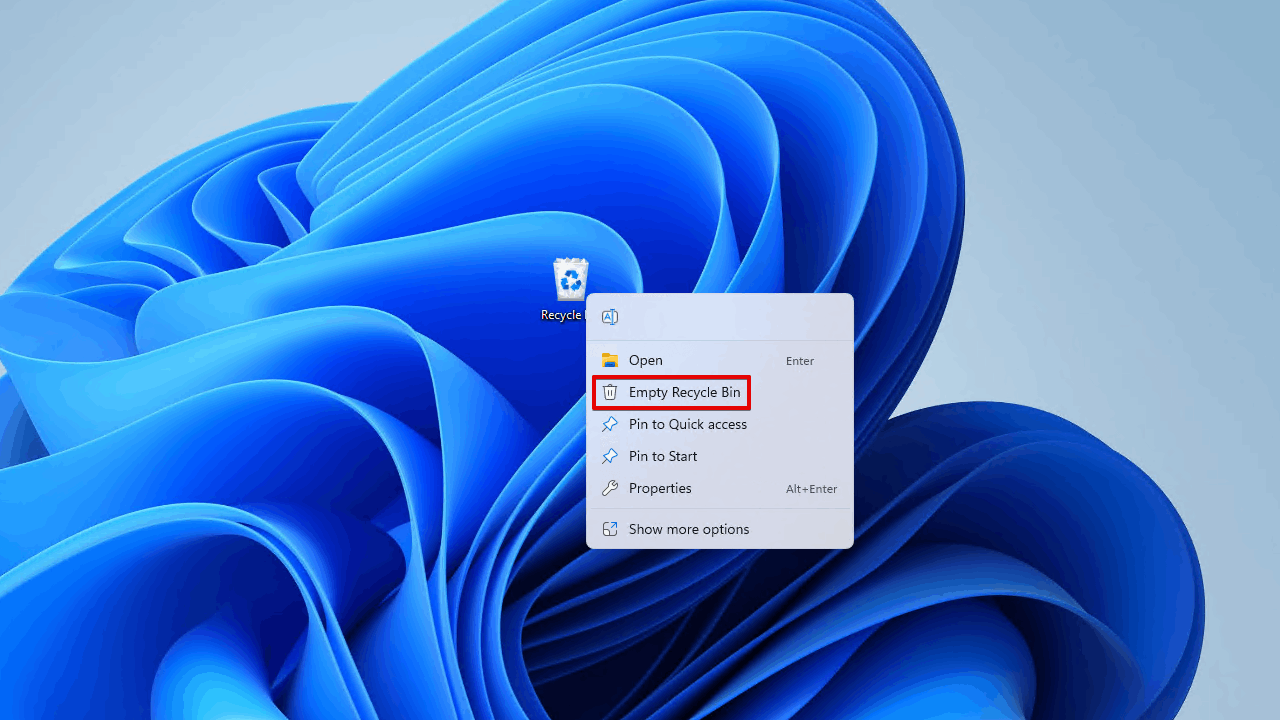
- Right-click Recycle Bin on your Desktop.

- Click Empty Recycle Bin.
Method 2: Check for Hidden Files and Folders
Some files and folders on your computer may be marked with the Hidden attribute, so they won’t appear in File Explorer unless a specific setting is enabled. You can delete any hidden personal data that’s taking up space, but be careful not to delete any essential system files that may also be hidden. If you do happen to delete some hidden data that you weren’t supposed to, you can recover the hidden files if necessary.
Here’s how you can make hidden data visible on Windows:
- Open File Explorer.
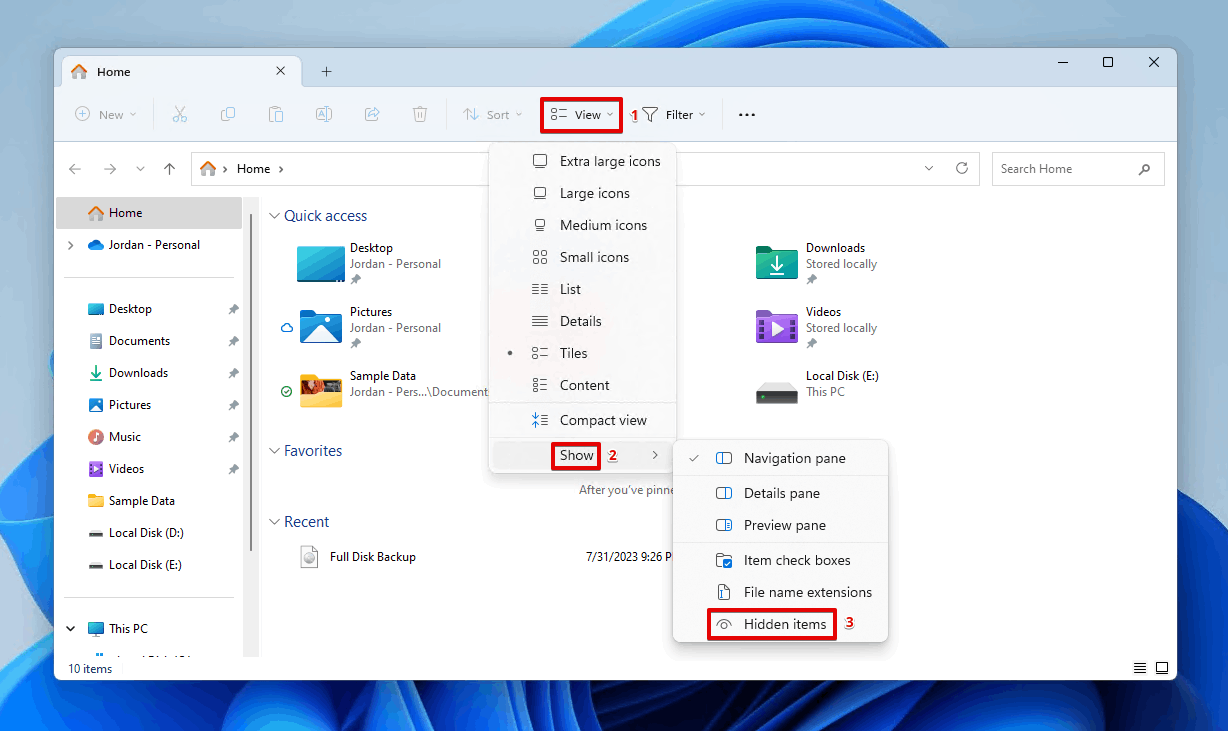
- Click View, then hover Show and click Hidden items.
Method 3: Run Disk Cleanup In Windows
The Disk Cleanup feature that’s included with Windows can be used to quickly delete any unwanted files on your drive to clear up some storage space.
We’ll show you how to run it and delete any data you don’t want:
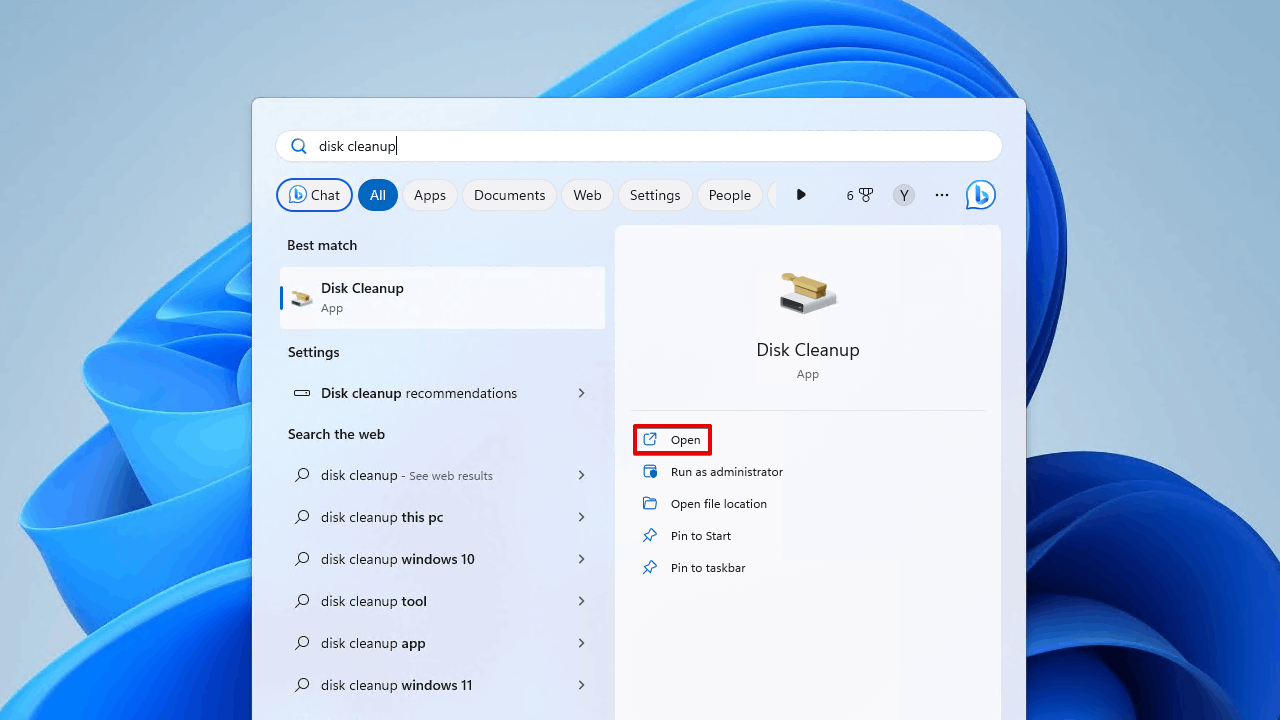
- Click Start. Search “Disk Cleanup” and open it.
- Select the drive you wish to clean up. Click OK.
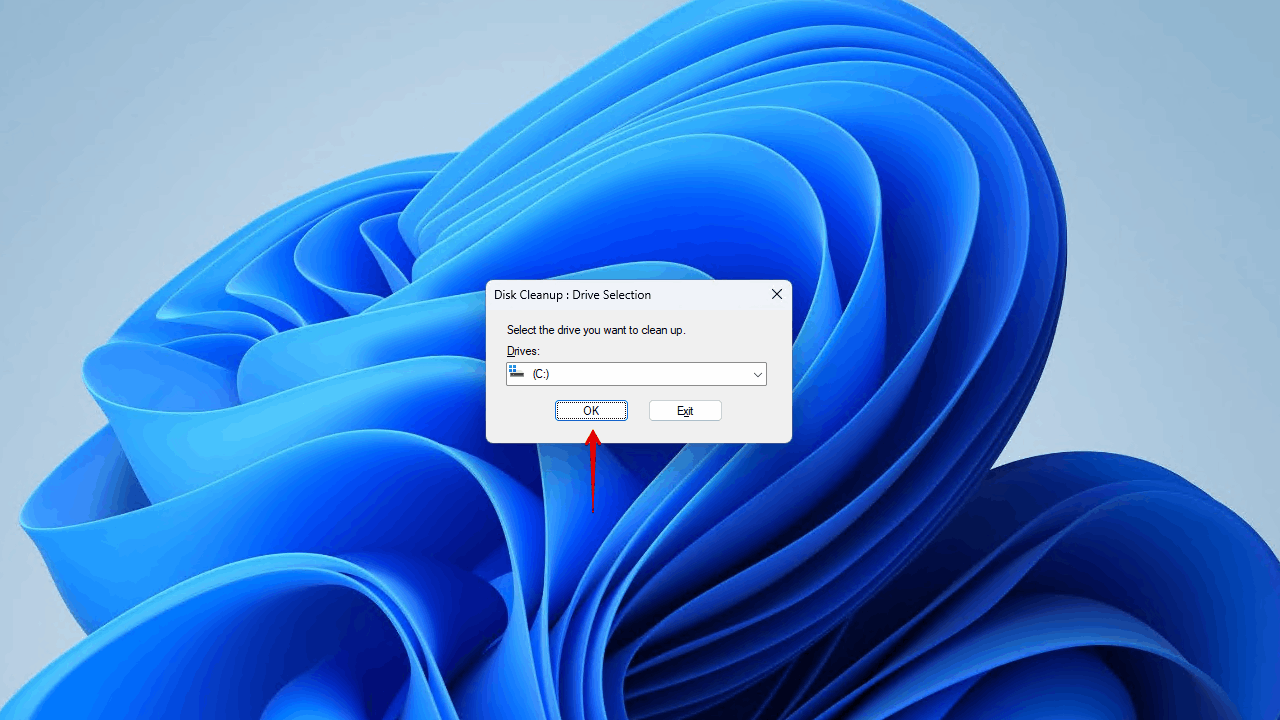
- Select what you wish to clean up, then click OK.
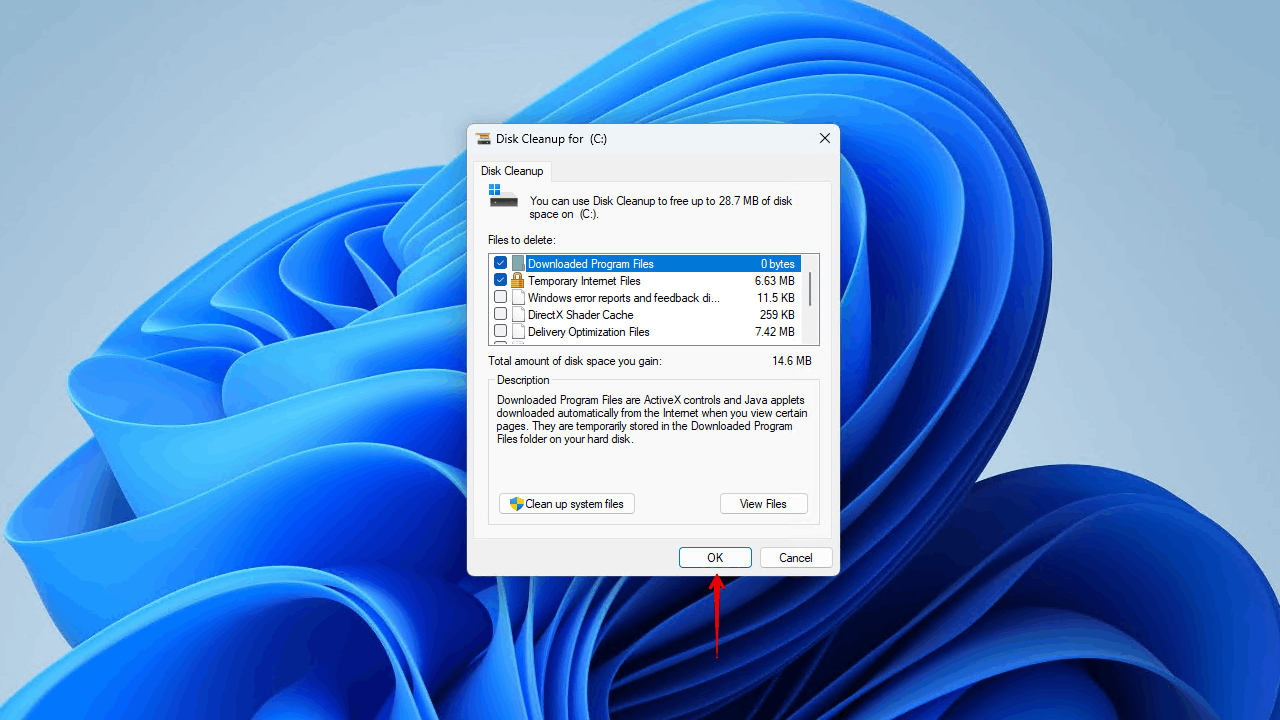
- Click Delete Files to confirm.
You can perform the same procedure and click Clean up system files (found in step 3) to also delete any unnecessary system files that still remain on the drive.
Method 4: Clean Temporary Files and Cache
Third-party tools, like CCleaner, can also be used to clean up temp files on the drive, freeing up some storage space. This is helpful if the hard drive is almost full but you can’t find the files and it takes away the stress of trying to determine what files can and cannot be deleted.
Here’s how you clean out temporary files using CCleaner:
- Download and install CCleaner.
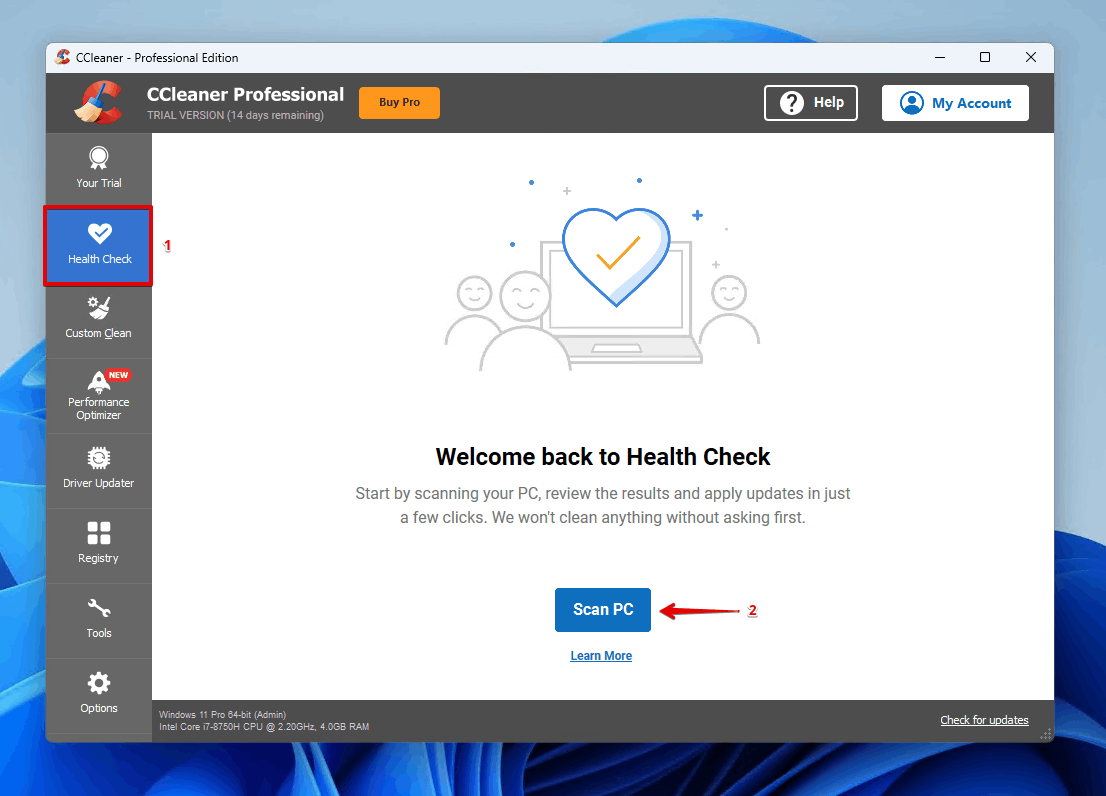
- Click Health Check, then Scan PC.
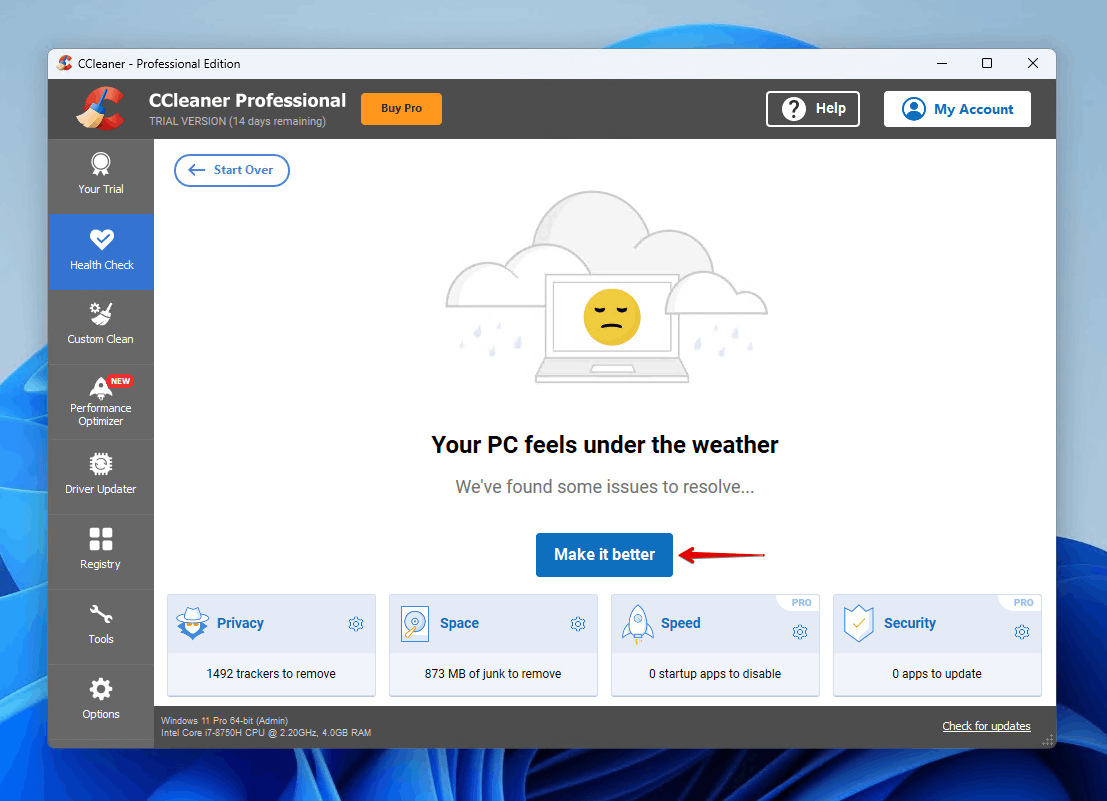
- Click Make it better.
A more advanced approach is using WinDirStat, which shows you a full breakdown of what files are using the most space on your drive, which includes both personal and system files.
Method 5: Scan for Malware and Viruses
Viruses can perform a number of terrible things to your computer, like consuming valuable resources and ramping your disk usage up to 100%. If your drive has been infected with a virus that is designed to consume disk space, you should perform an antimalware scan.
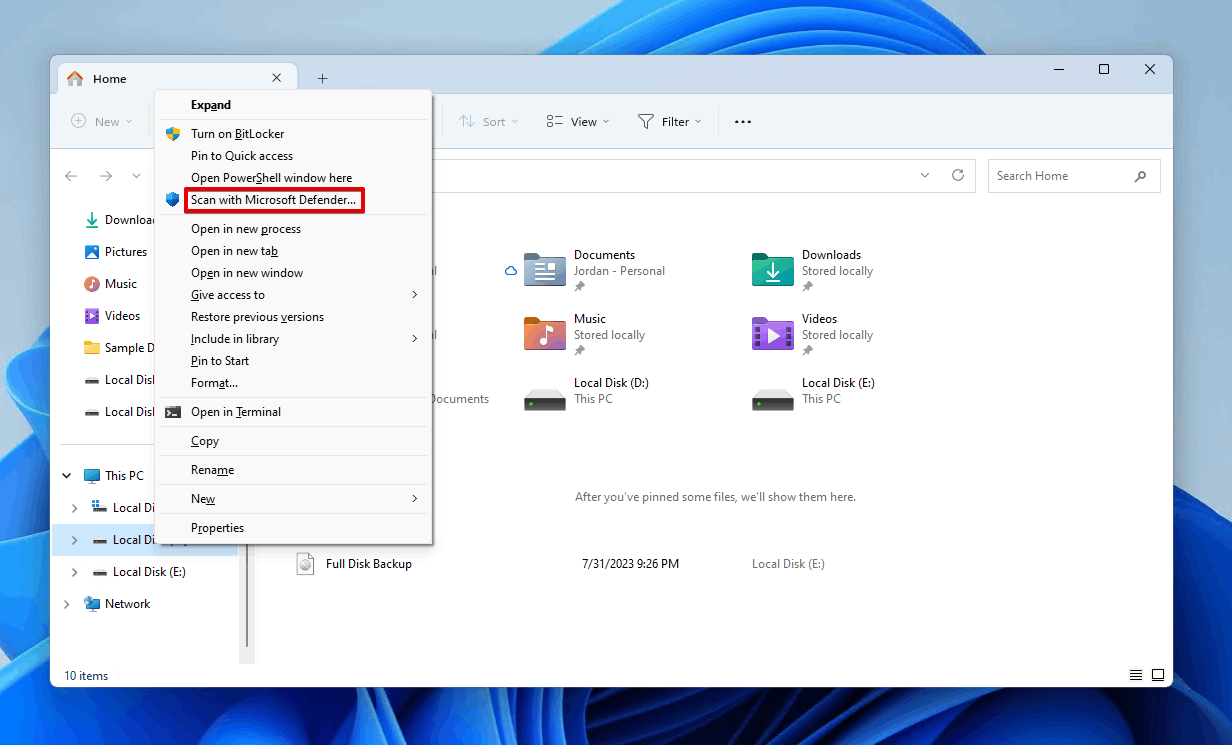
- Open File Explorer.
- Shift right-click the drive, and click Scan with Microsoft Defender.
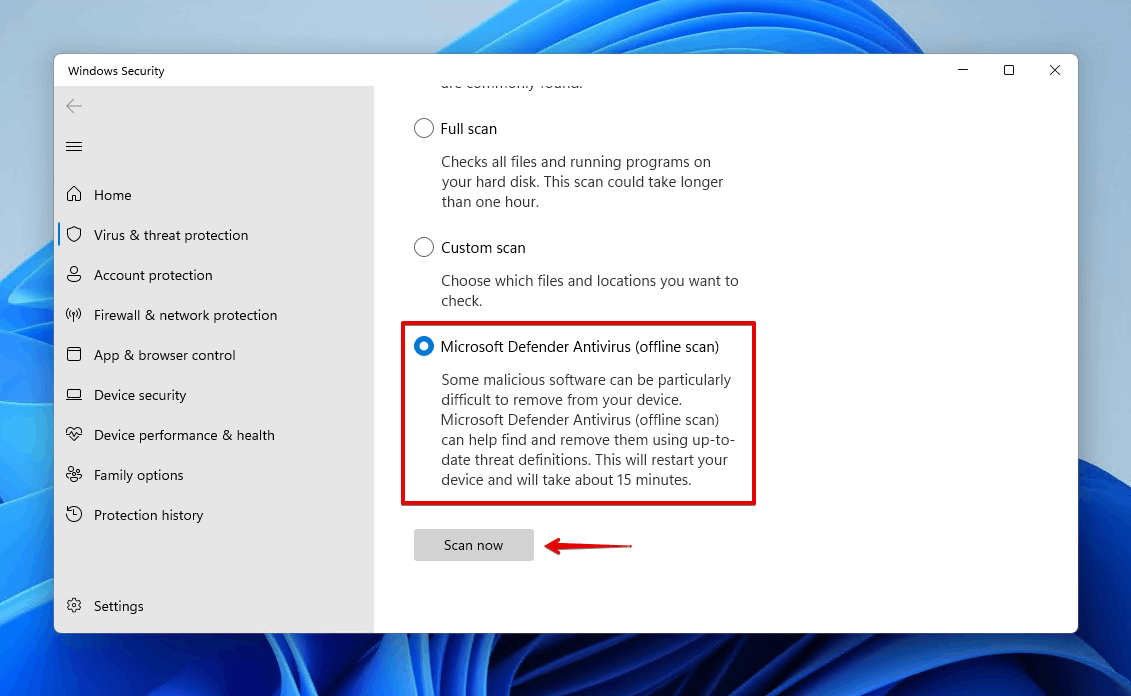
- To perform a more comprehensive scan, select Microsoft Defender Antivirus (offline scan), and click Scan now.
If a virus has infected your drive and corrupted it, follow our guide on how to fix a corrupted hard drive.
Method 6: Delete Unnecessary System Backup Files
If system protection is enabled, Windows will make restore points after certain events take place. These restore points can be used to restore your system to working condition if it stops working. The problem with these restore points is that they can take up valuable disk space. You can free up some storage space by deleting them.
- Click Start. Search “Control Panel” and open it.
- Switch the view to Large icons.
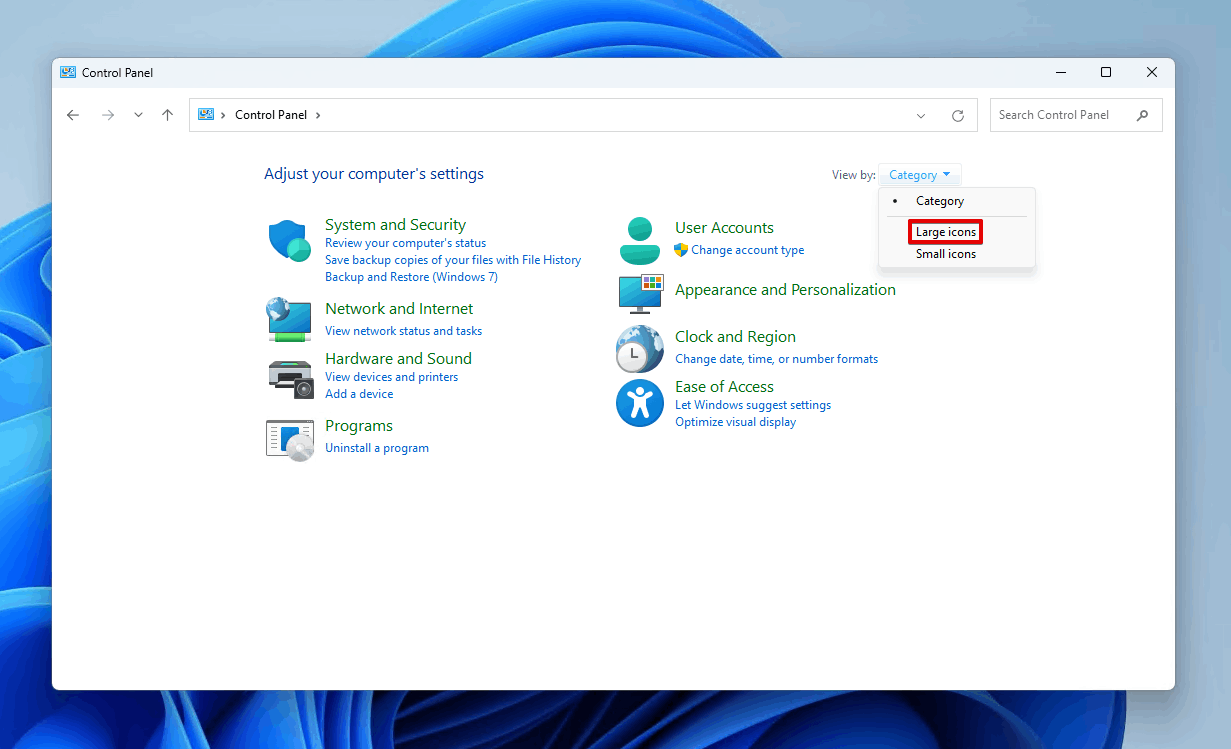
- Click Recovery.
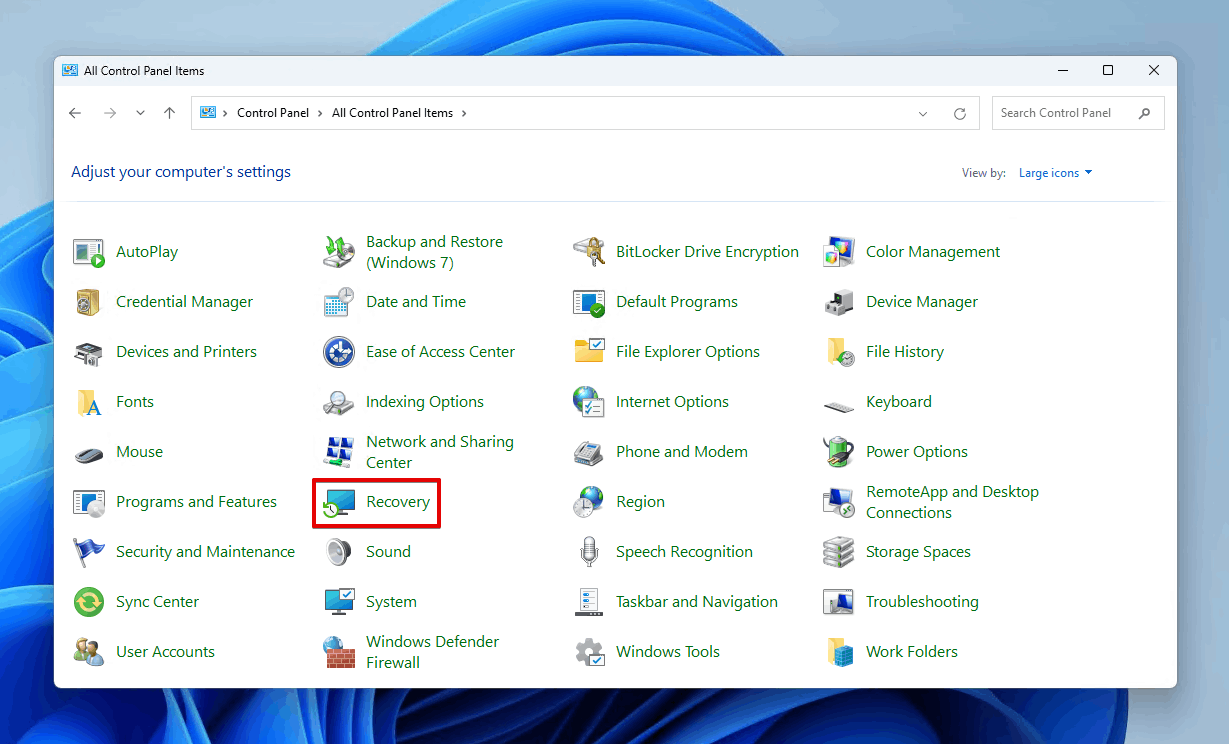
- Click Configure System Restore.
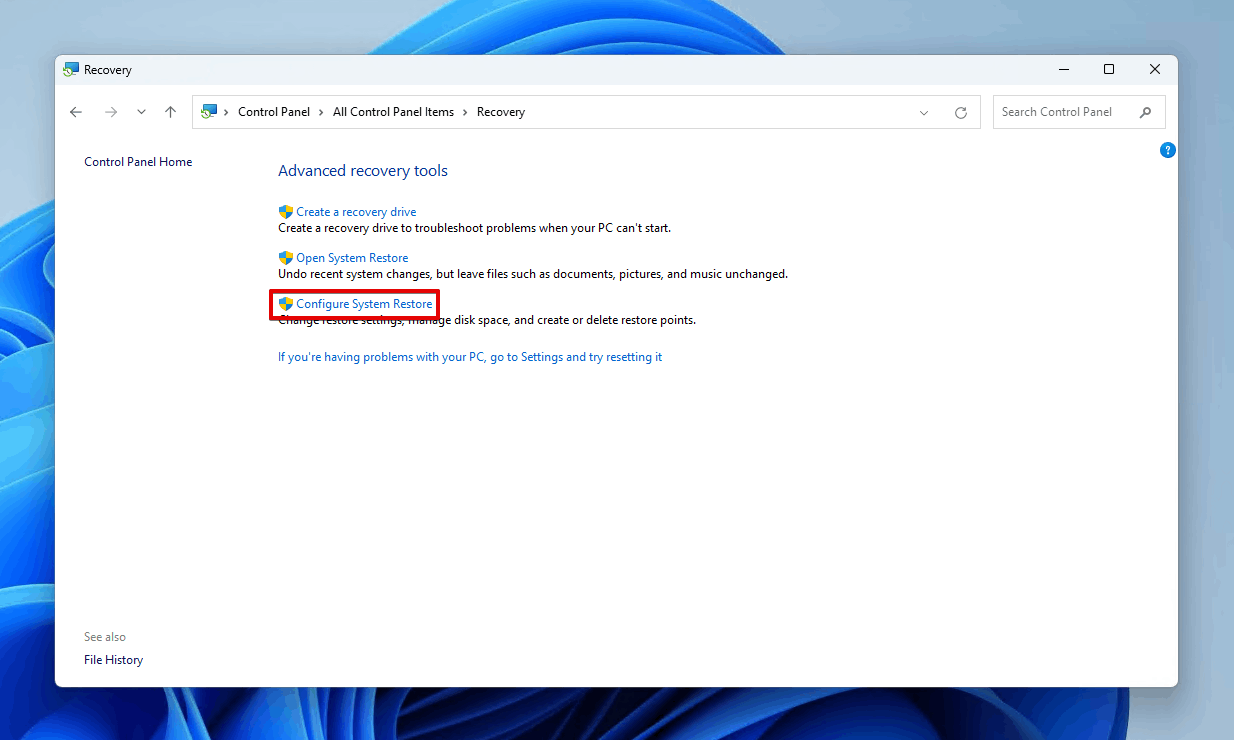
- Click Configure.
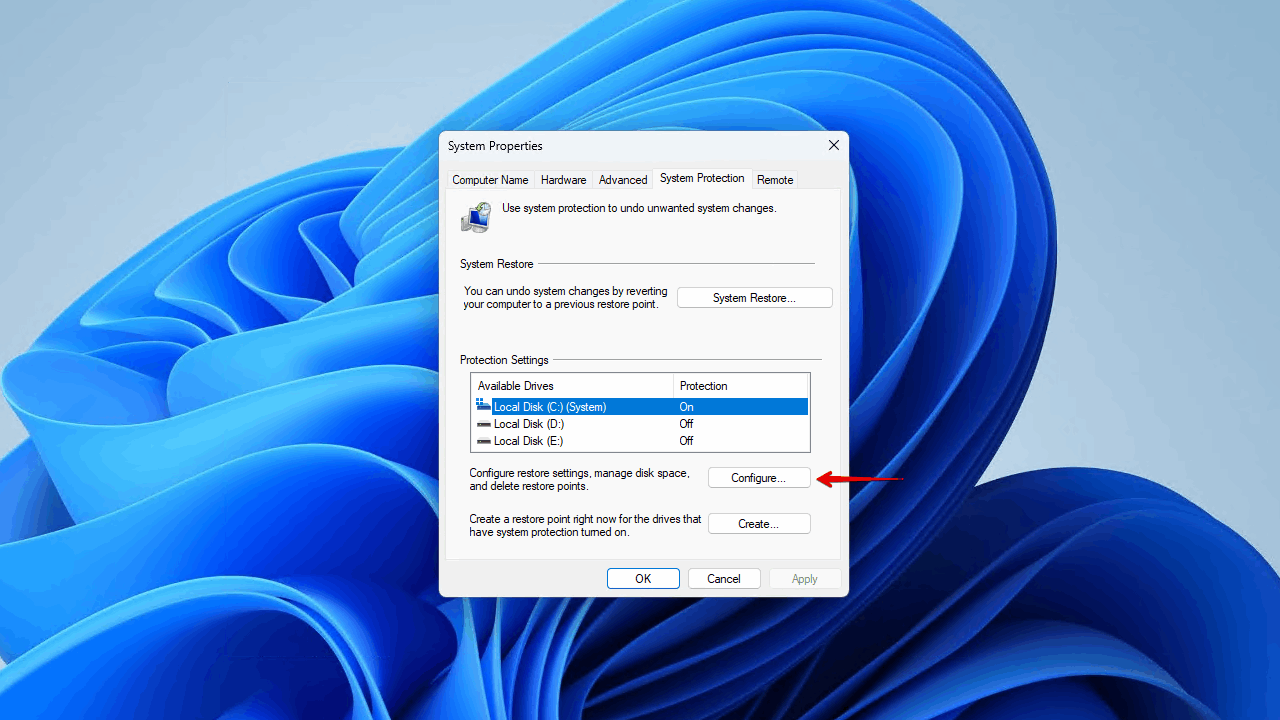
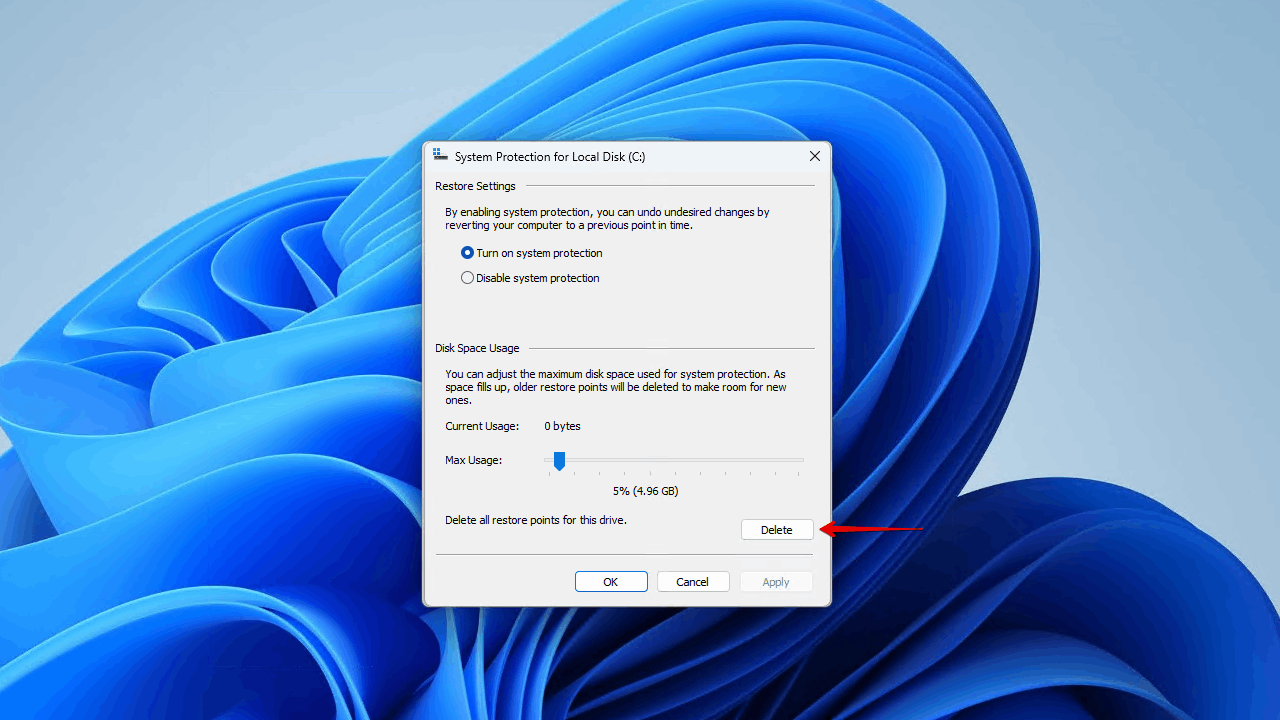
- Click Delete.
- Click Continue.
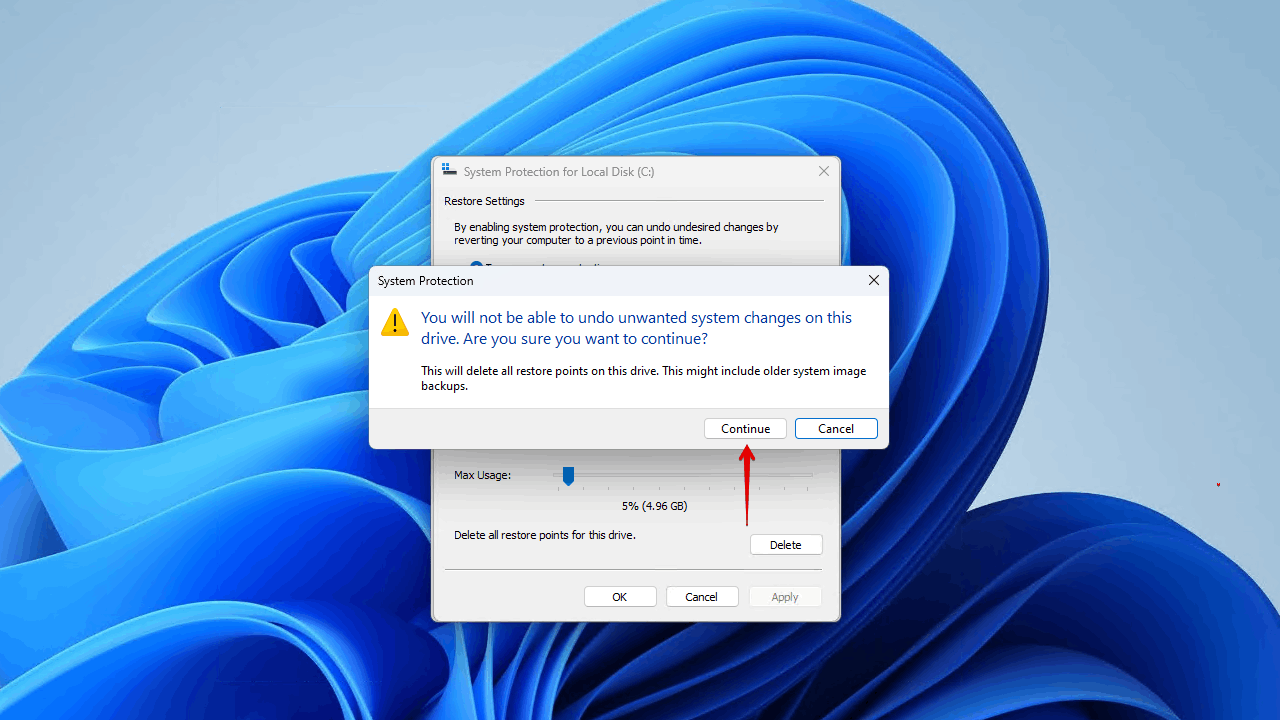
To manage this going forward, you may want to adjust the Max Usage slider found in step 6, as it will limit how much space the restore points can take.
Method 7: Check Your Reserved Storage Preferences
If your local disk is full, but no files are available for you to delete, you should check how much space is being used for Reserved Storage. Windows reserves a portion of your disk to help with performance and the proper installation of Windows updates.
Follow these steps to see how much space Windows has reserved:
- Right-click Start and click Settings.
- Click Storage (found in System).
- Click Show more categories.
- Click System & reserved.
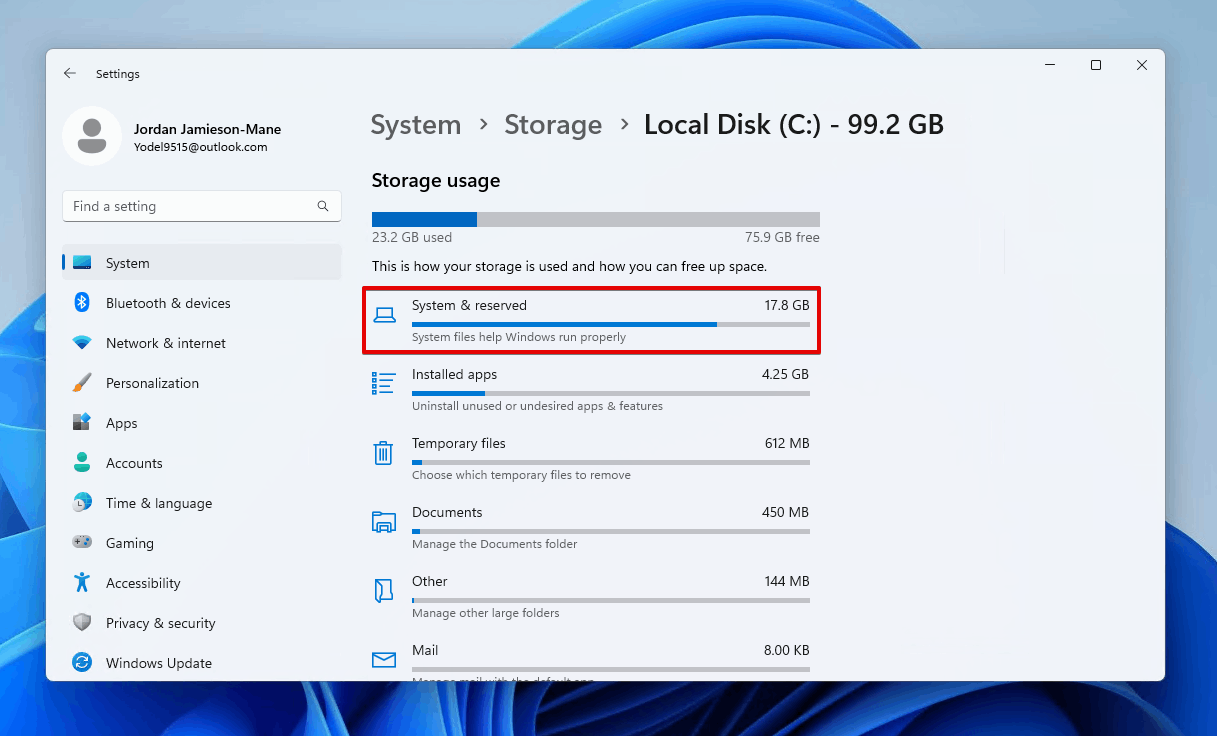
As you’ll notice, there is no way to limit how much space Windows uses. However, you can reduce it by uninstalling optional features. Here’s a brief guide on how to do so to help fix the ‘hard disk full but no files’ Windows 10 and 11 issue:
- Return to the Settings window and click Apps.
- Click Optional features.
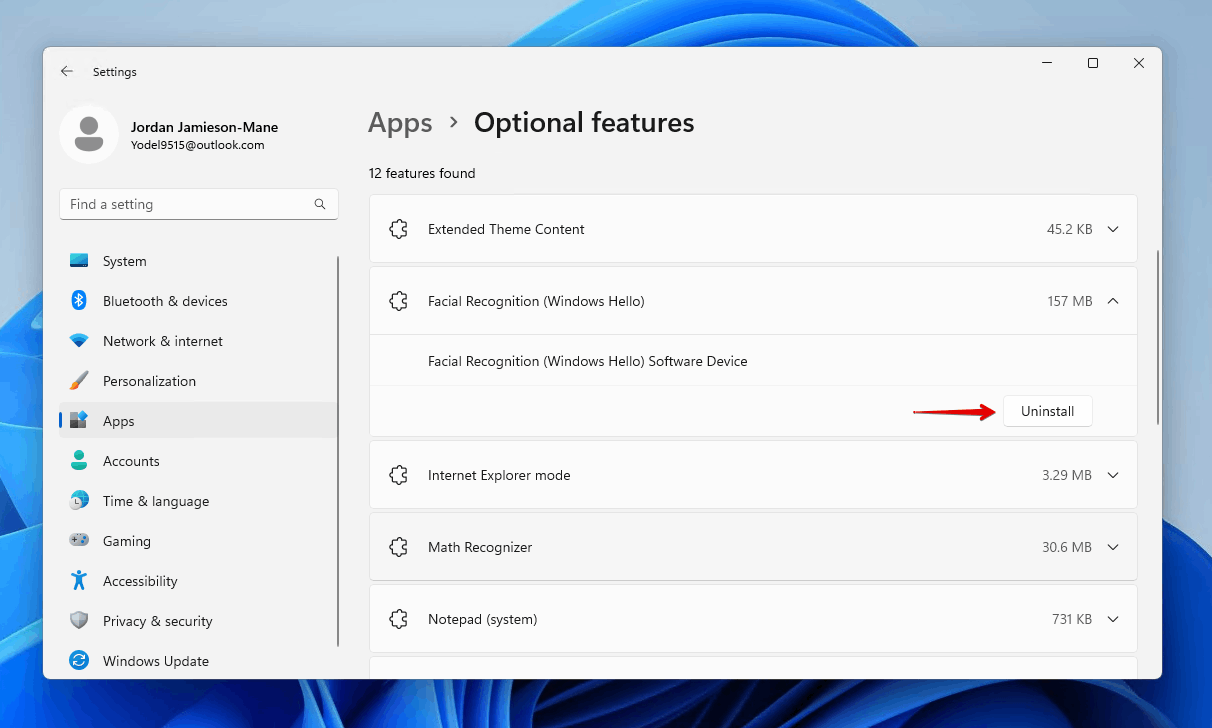
- Uninstall any unnecessary optional features.
Method 8: Fix Hard Drive Errors
To fix a disk space issue that is being caused by a hard drive issue, you may be able to repair the problem using the command CHKDSK.
Follow these instructions to run CHKDSK and address any problems your hard drive is facing:
- Right-click Start and click Terminal (Admin).
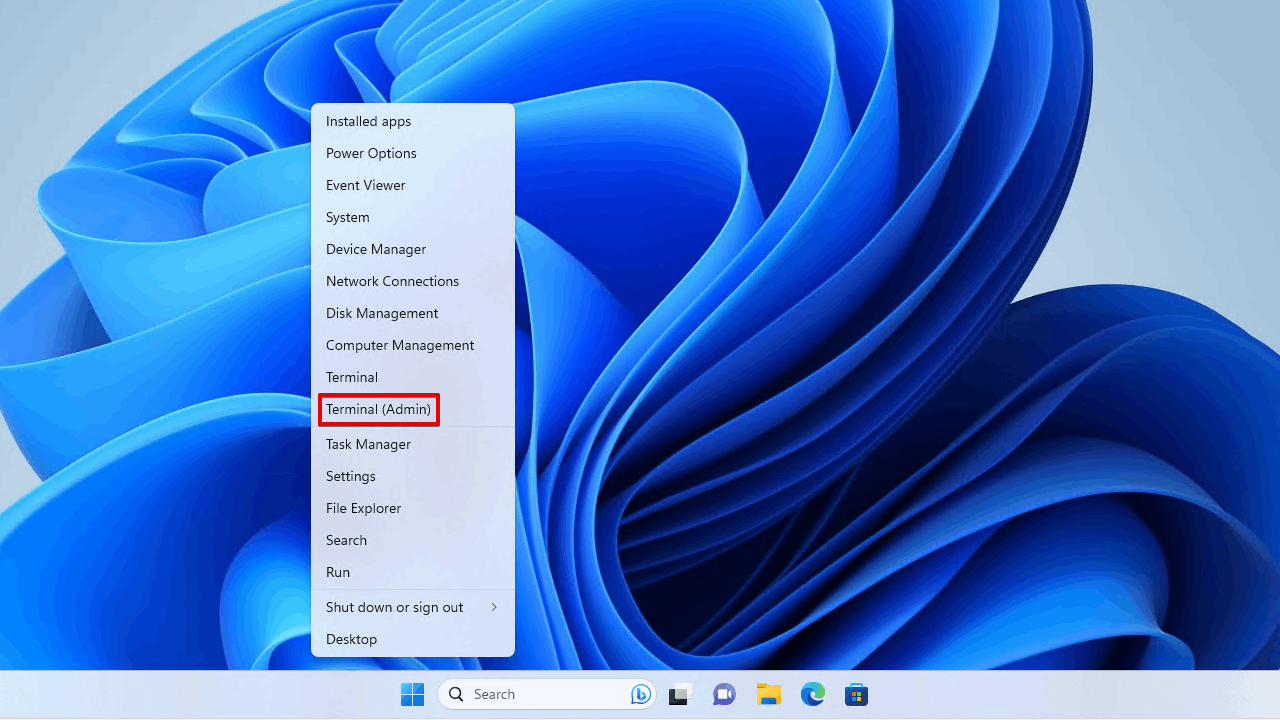
- Type chkdsk *: /r. Be sure to replace * with the letter assigned to the drive you wish to run it on. Press Enter.
Method 9: Format Your Hard Drive
Performing a format is the fastest way to clear up data on your drive. This is because a format deletes every file on the drive or partition. If you don’t care about the data on the disk, you can format it as a means of quickly freeing up the entire drive.
If you intend to format a hard drive but you wish to keep your data, see our guide on how to format a hard drive without losing data.
This is how you format a drive through Disk Management:
- Right-click Start and click Disk Management.
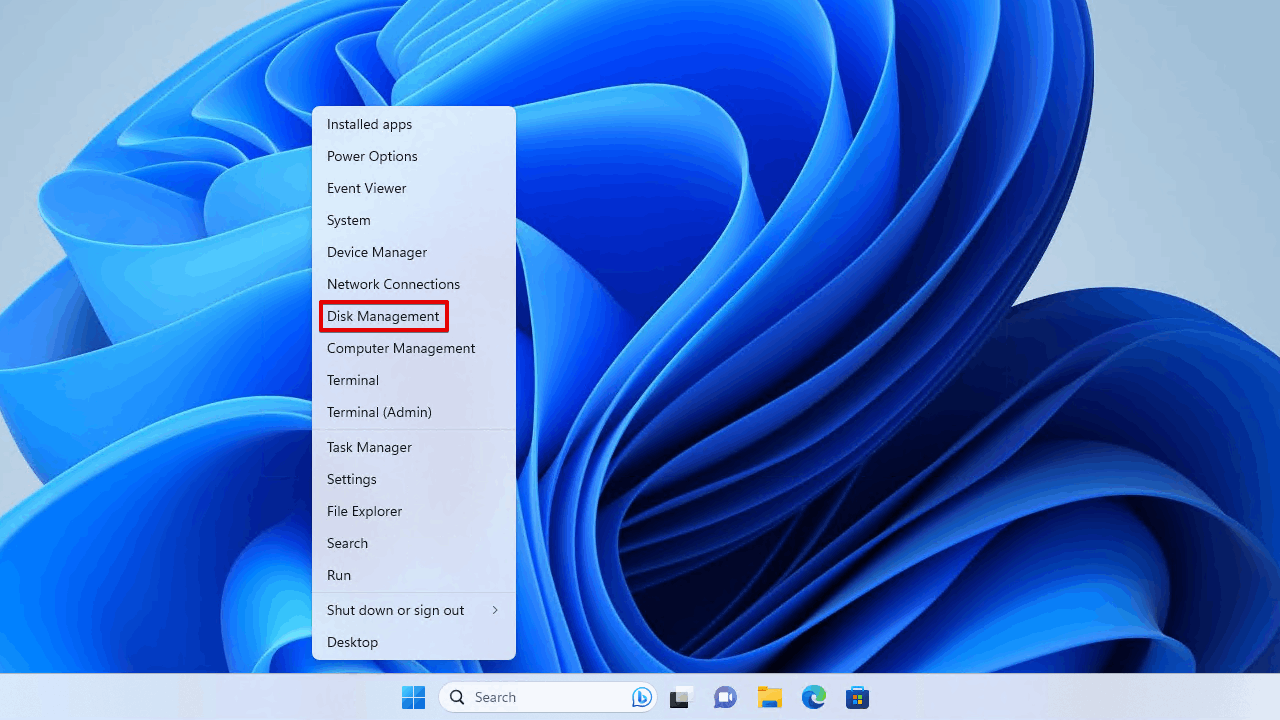
- Right-click the volume and click Format.
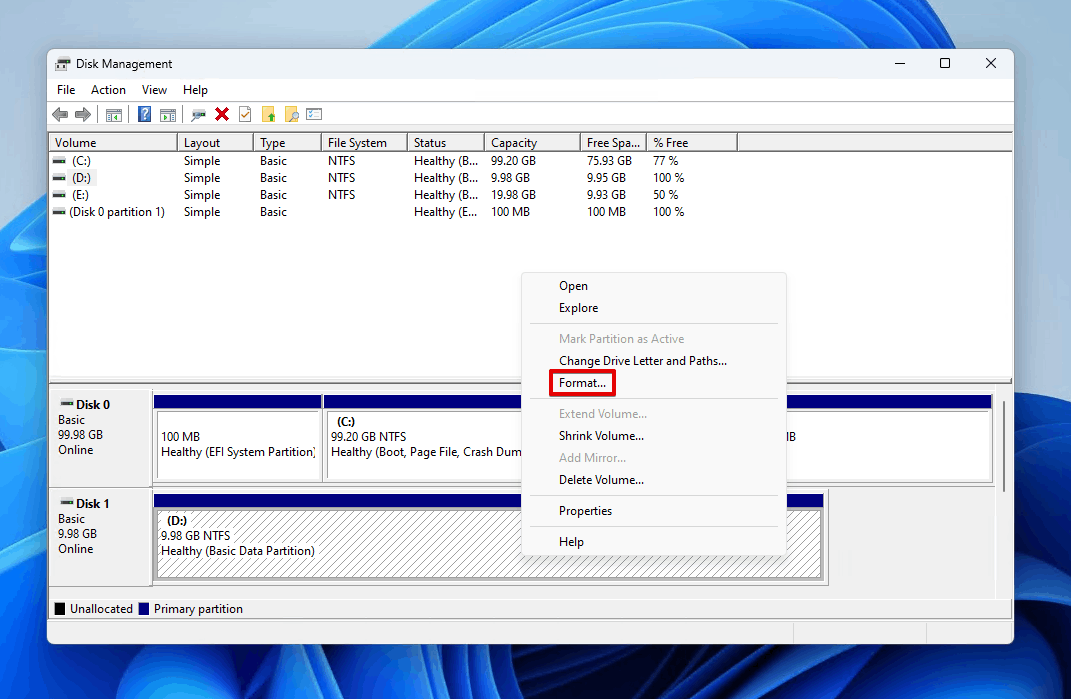
- Make sure Perform a quick format is ticked, then click OK.
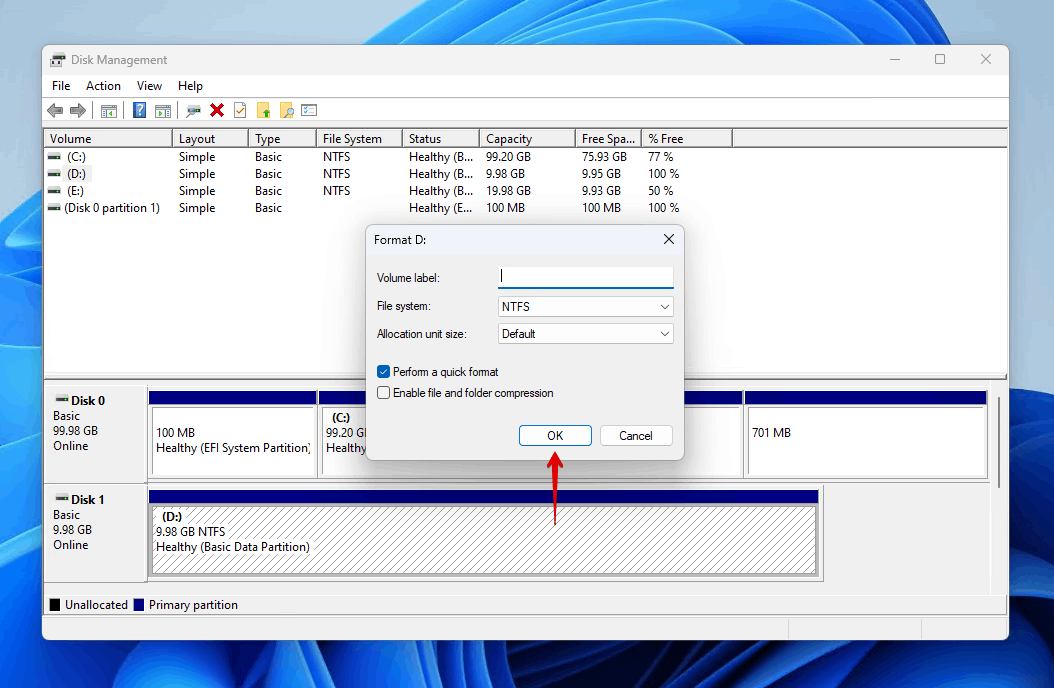
- Click OK to confirm.
Consider Reinstalling OS
When the problem resides with your system drive, formatting can be a bit more difficult. In these cases, you should reinstall the operating system. During the process, you can delete the existing volumes and set the drive up like you would a brand-new one. Just be sure to make a backup of all the data you want to keep, as it will be lost in the process.
FAQ
What to do if I am low on disk space but there is nothing to delete?
When a hard drive is full for no reason, it could be a problem with the drive or an overabundance of unnecessary temp files. You can use the Disk Cleanup utility to clear out files you can’t find. CCleaner can do something similar. If that doesn’t help, it could be a drive problem, so try to repair it with CHKDSK or perform a format.
Why does my external hard drive show used space but there are no files on it?
When your external hard drive starts telling you that it has no more space, even if there are no files on it, it may be due to corruption. If you know there are files on it that have disappeared, you should recover them now using data recovery software. Then, you can fix the drive by formatting it.
Why is C drive full for no reason?
Windows will always be installed on the C: drive. If your C: drive is full but no files can be deleted, it could be due to temporary files that haven’t been deleted. You can clear these up using the Disk Cleanup utility. Alternatively, you can move some essential files or applications to your D: drive, or any other additional drive you have. If you end up deleting some files that you weren’t supposed to, you can recover data from the C: drive to get it back.
How to fix Windows Server 2016 disk full but there are no files on it?
There is likely a large number of unnecessary files that can be deleted, some of which may even be hidden. Rather than seek them out and manually delete them, you can use the Disk Cleanup utility like you would with other versions of Windows.
- Click Start.
- Click Windows Administrative Tools, then launch Disk Cleanup.
- Follow the onscreen instructions to target the drive you wish to clean up and what files to delete.
Conclusion
The ‘hard disk full but no files’ problem in Windows 11 can be in relation to a number of problems, like drive errors, temporary files, and malware. You should start with data recovery if you know that data was on the drive. If you’ve been unable to get the data back from the drive, consider consulting a data recovery service for expert advice.
Once your data is recovered, clear up unnecessary files by emptying Recycle Bin and running the Disk Cleanup tool. Remove any viruses that are present with Microsoft Defender (or another antimalware tool) and fix drive errors using CHKDSK or by formatting. Going forward, it’s a good idea to regularly check your hard drive health to make sure you’re aware of any issues as they arise.
This article was written by Jordan Jamieson-Mane, a Staff Writer at Handy Recovery Advisor. It was also verified for technical accuracy by Andrey Vasilyev, our editorial advisor.
Curious about our content creation process? Take a look at our Editor Guidelines.
